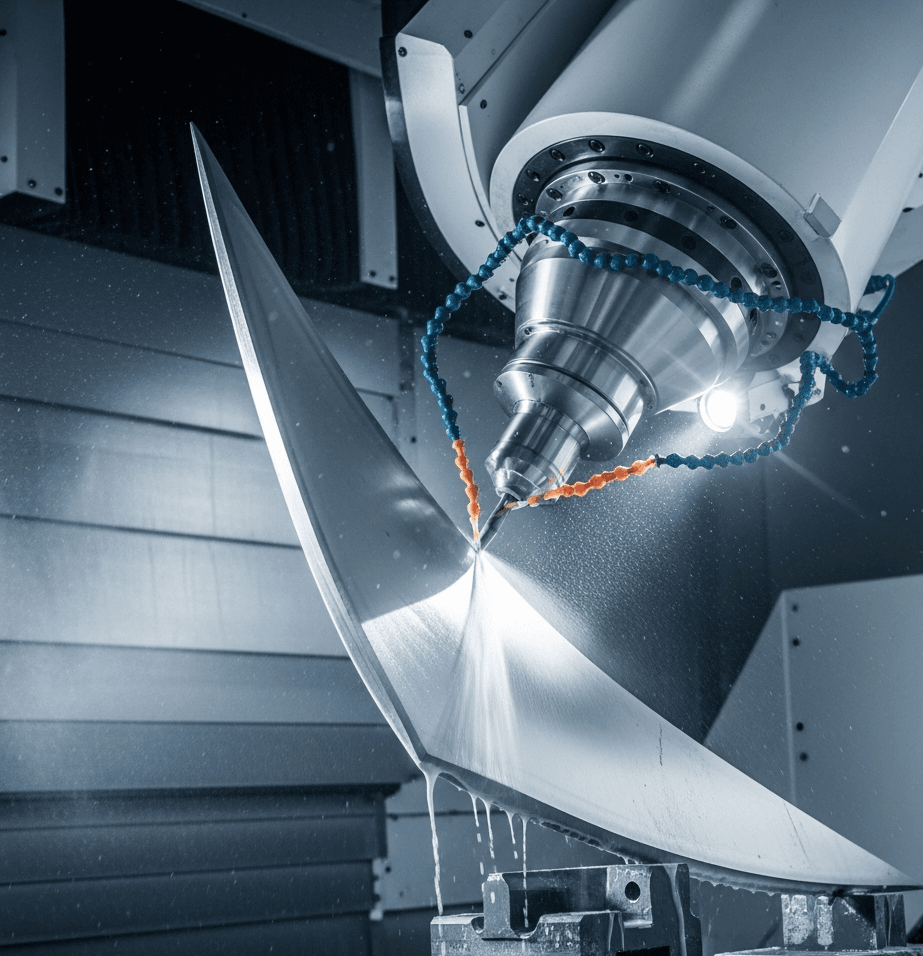
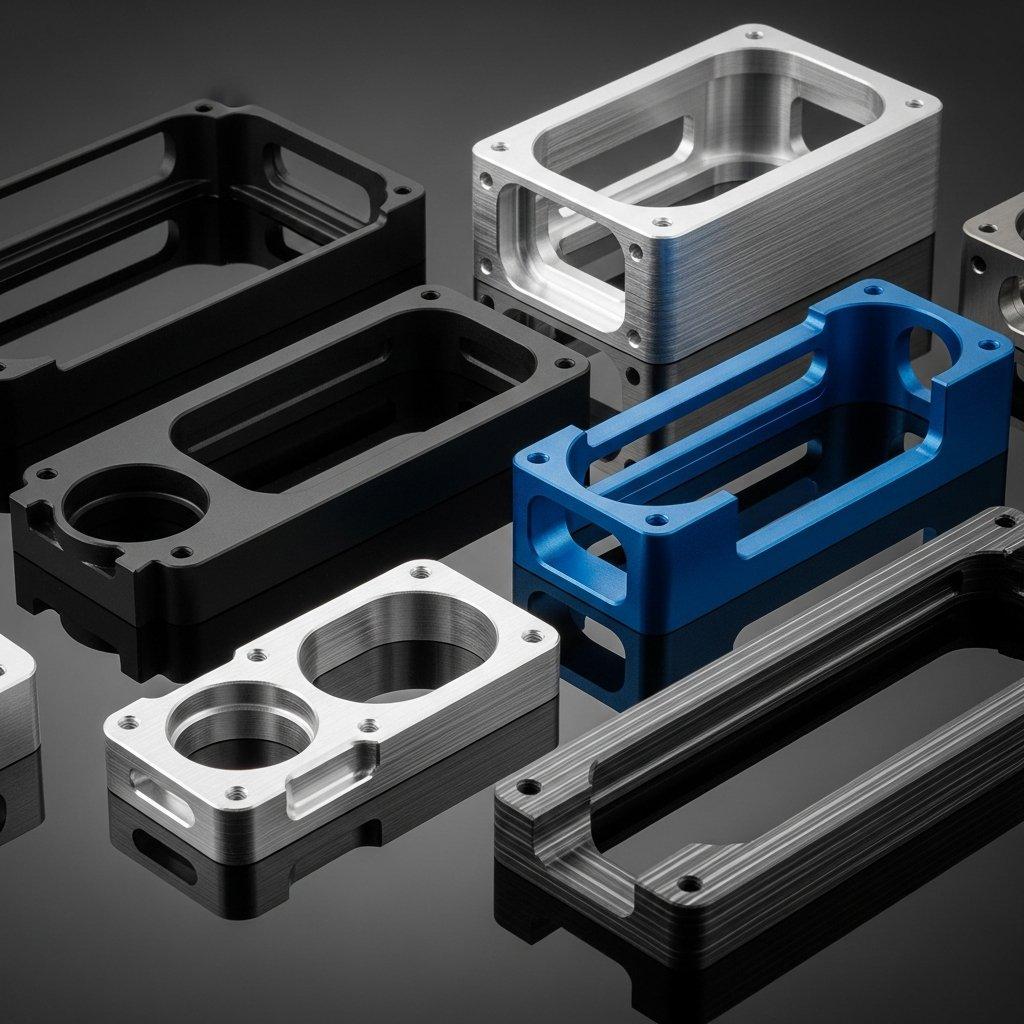
You have a critical part to produce, but you’re facing the complex world of CNC machining. The technical jargon surrounding 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis systems can be bewildering. Making the wrong choice isn’t just a simple mistake; it can lead to catastrophic budget overruns, unacceptable delays in your production schedule, and a final component that fails to meet crucial quality and design specifications.
Imagine the frustration of paying a premium for a 5-axis CNC machining service when a simpler 3-axis process would have been perfectly sufficient, wasting valuable capital. Or worse, picture receiving a batch of complex parts marred by inaccuracies because they were produced on a 3-axis machine that required multiple, error-prone manual adjustments. This isn’t just a manufacturing headache; it’s a direct threat to your project’s success, your product’s integrity, and your reputation.

This definitive guide eliminates the confusion. We will thoroughly demystify 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling, providing a clear and comprehensive breakdown of each technology. By understanding the core capabilities, ideal applications, and cost implications, you will be empowered to select the most efficient and cost-effective CNC machining solution. Partner with an expert like ly-machining to ensure your project is done right, on time, and within budget, delivering the superior quality your design deserves.
Featured Snippet: How to Choose the Right CNC Machine
Choosing the correct CNC machine hinges on four factors: part complexity, required precision, budget, and lead time. For parts with simple, planar geometries, 3-axis CNC machining is the most economical choice. If your component requires machining on multiple faces or has angled features, 4-axis CNC machining offers a balance of capability and cost. For parts with highly complex contours, deep undercuts, and the strictest tolerance demands, 5-axis CNC machining provides unparalleled precision and efficiency, justifying its higher cost.
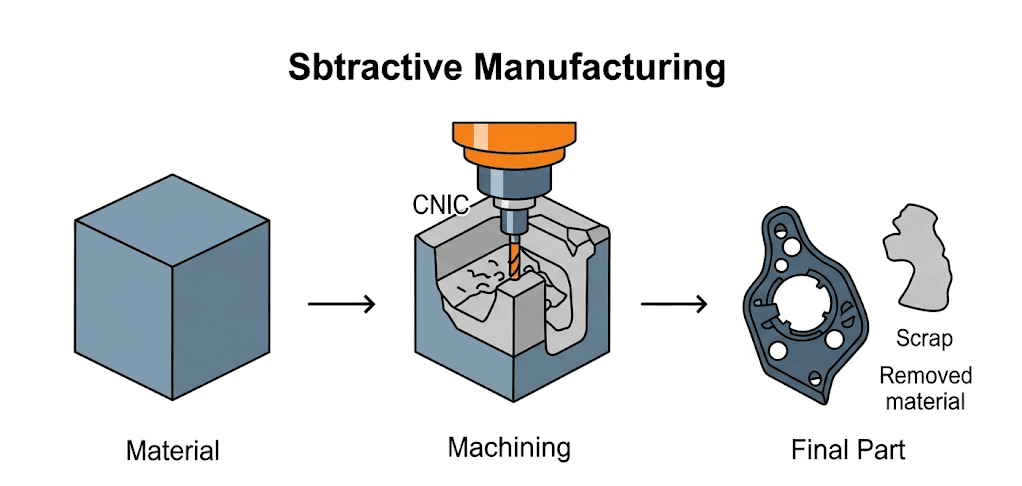
From Technical Jargon to Informed Decisions
Navigating the options in modern manufacturing is essential for optimizing your production process, from prototype to full-scale launch. Therefore, a solid understanding of the fundamental differences between these CNC milling technologies is your greatest asset. Subsequently, this knowledge will not only guide your selection but also facilitate clearer communication with your manufacturing partner. Ultimately, a well-informed decision-making process is the foundation for a seamless production experience and the highest quality final parts for all your CNC machining projects. This guide will provide that foundation.
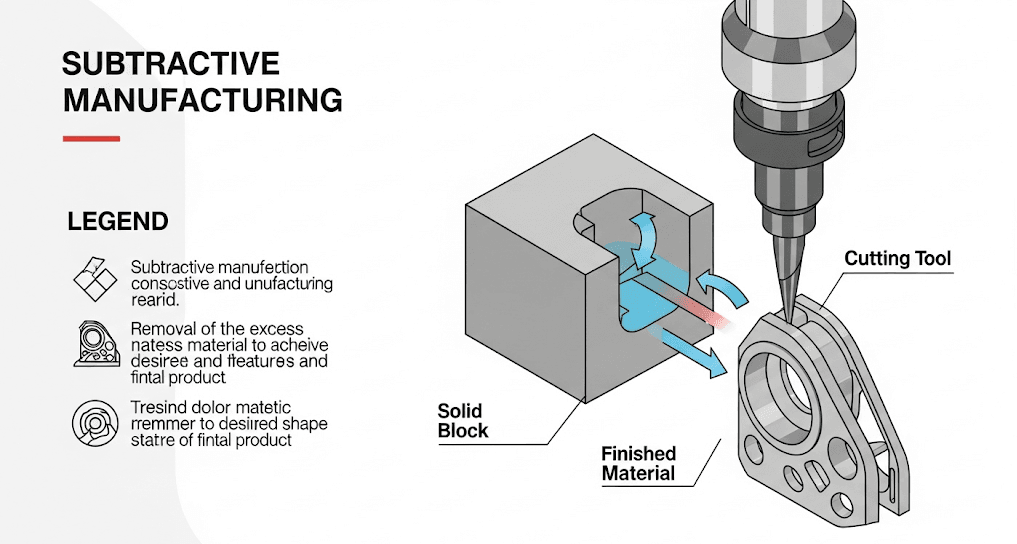
The Core of the Craft: What is CNC Machining?
Before diving into the axes, it’s crucial to understand what CNC machining is. CNC, or Computer Numerical Control, is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses computer-programmed instructions to control high-speed cutting tools. Essentially, a machine is given a digital blueprint (a CAD file) and automatically carves a custom part out of a solid block of material (like aluminum, steel, or plastic), removing material layer by layer until the final shape is achieved.
This process is guided by G-code, the programming language of CNC machines, which dictates the tool’s movement, speed, and tool changes. The result is a highly precise, repeatable, and efficient method for producing components that would be incredibly difficult or impossible to create by hand. The primary difference between 3, 4, and 5-axis machines lies in the freedom of movement they possess to perform this subtractive process.
The Workhorse: A Deep Dive into 3-Axis CNC Machining
3-axis CNC milling is the most common and foundational type of CNC machining. In this setup, the cutting tool operates along three linear axes:
- X-axis: Left to right
- Y-axis: Front to back
- Z-axis: Up and down
The workpiece remains fixed in a single position while the tool moves around it. This approach is highly effective and cost-efficient for parts with relatively simple geometries.
Ideal Applications for 3-Axis CNC Machining: This method excels at producing parts that can be machined from a single side. Common applications include:
- Facing and Pocketing: Creating flat surfaces or shallow cavities.
- Drilling and Tapping: Precisely boring holes and creating threads.
- Slots and Grooves: Cutting channels into a part’s surface.
- Component Housings & Brackets: Manufacturing parts with primarily 2.5D features.
Limitations and Workarounds: The primary limitation of 3-axis machining is that it cannot access all sides of a part in a single setup. For parts with features on multiple faces, the operator must manually unclamp, rotate, and reclamp the workpiece. This process introduces the risk of slight positioning errors (tolerance stacking) and increases labor time. However, for many designs, it remains the most economical CNC milling solution.
The Next Level: A Deep Dive into 4-Axis CNC Machining
4-axis CNC machining introduces a rotational dimension to the standard three linear axes. This is achieved by adding an A-axis (or sometimes a B-axis), which allows the workpiece itself to rotate. This single addition dramatically expands the machine’s capabilities, bridging the gap between simple parts and highly complex ones.
There are two main types of 4-axis machining:
- Indexing 4-Axis: The A-axis rotates the part to a specific angle, then locks in place. The machine then performs 3-axis milling operations. This is repeated for each face that needs work.
- Continuous 4-Axis: The machine can move the cutting tool along the X, Y, and Z axes while simultaneously rotating the part on the A-axis. This allows for the creation of complex helical geometries.
When to Choose 4-Axis Over 3-Axis: Opt for 4-axis CNC machining when your part has features that are not on the top or bottom surface. It eliminates the need for multiple manual setups, which directly translates to:
- Improved Accuracy: The part is not moved, so precision between features on different faces is much higher.
- Reduced Lead Time: Automating the rotation is significantly faster than manual repositioning.
- Expanded Capability: Ideal for machining holes on the side of a cylinder, cams, gears, and propellers.
The Pinnacle of Precision: A Deep Dive into 5-Axis CNC Machining
5-axis CNC machining stands at the apex of manufacturing technology. It utilizes the three linear axes (X, Y, Z) plus two additional rotational axes, allowing the cutting tool and/or the workpiece to be moved and tilted in concert. This provides an almost limitless range of tool angles, enabling the creation of exceptionally complex parts in a single setup—a concept often referred to as “Done-in-One” manufacturing.
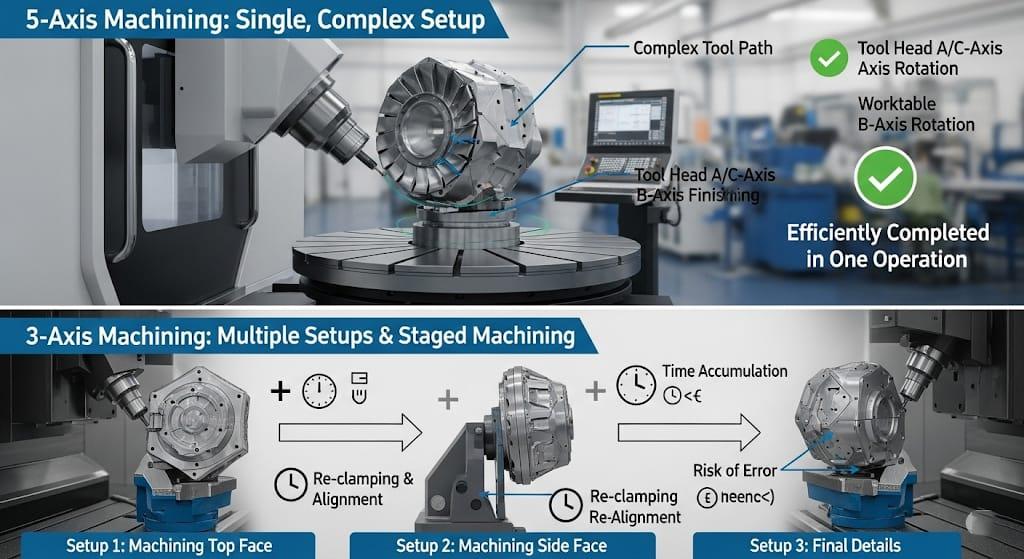
The two primary types of 5-axis machining are:
- 3+2 Axis Machining (Positional 5-Axis): The machine uses the two rotational axes to orient the cutting tool at a fixed, tilted angle relative to the workpiece. It then performs 3-axis milling operations. This is highly efficient for machining multiple angled features without needing continuous tool movement.
- Continuous 5-Axis Machining: All five axes move simultaneously, allowing the tool to follow complex, contoured surfaces smoothly. This is essential for achieving the superior surface finishes required for molds, turbine blades, and medical implants.
Industry-Specific Applications:
- Aerospace: Machining intricate impellers, turbine blades, and structural components with complex curves.
- Medical: Creating custom orthopedic implants, surgical tools, and prosthetics with organic shapes.
- Automotive: Prototyping engine blocks, cylinder heads, and high-performance components.
While the programming complexity and machine cost are higher, the benefits in terms of capability, accuracy, and speed for complex parts are unmatched.
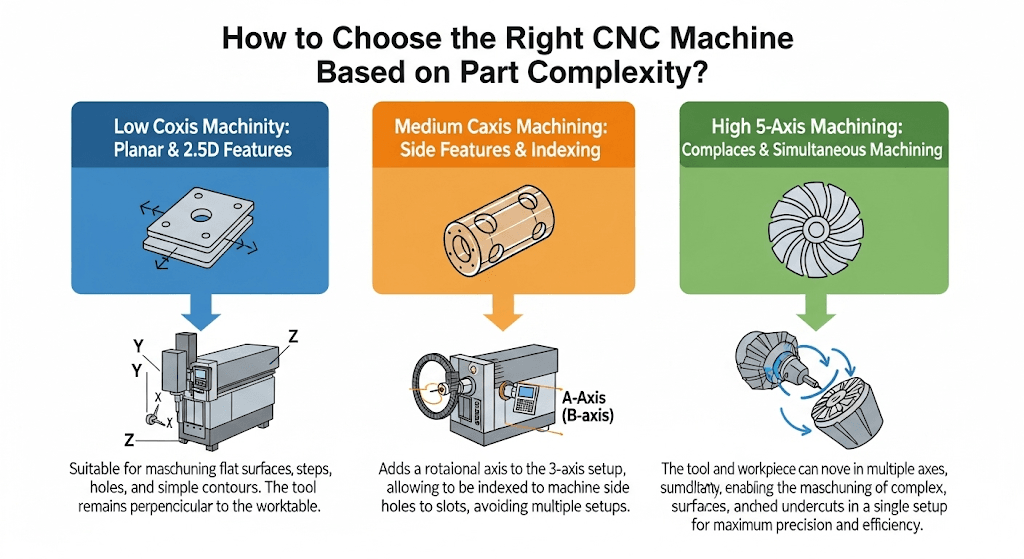
Decision Framework: How to Choose the Right Process
Selecting the right CNC machining process is a strategic decision. Use this step-by-step framework to ensure you make the optimal choice for your project.
- Analyze Part Geometry:
- Is it simple and planar? Can all features be accessed from a single direction? -> 3-Axis is likely best.
- Does it have features on the sides? Is it cylindrical with slots or holes? -> 4-Axis offers greater efficiency and accuracy.
- Does it have complex curves, deep pockets, or angled features on multiple faces? -> 5-Axis is probably necessary.
- Define Tolerance Requirements:
- Standard tolerances are achievable on all machines. However, if features have very tight positional tolerances relative to each other across different faces, minimizing setups is key.
- High Precision: 4-axis and 5-axis machining reduce the tolerance stacking that occurs with multiple setups on a 3-axis machine.
- Evaluate Production Volume & Lead Time:
- For a single complex prototype, the programming time for a 5-axis machine may be significant.
- For a production run of complex parts, the efficiency gained from single-setup 5-axis machining drastically reduces the per-part cycle time and overall lead time.
- Balance Budget vs. Capability (Cost Analysis):
- Machine Time Cost: The hourly rate increases from 3-axis to 5-axis.
- Setup Cost: 3-axis may have lower initial programming but higher labor costs for multiple setups. 5-axis has higher upfront programming costs but virtually eliminates setup labor for complex parts.
- Overall Cost: Don’t just look at the hourly rate. For a complex part, a 5-axis machine can be cheaper overall because it produces a finished part faster and with less risk of scrap.
CNC Machining Axis Comparison
| Attribute | 3-Axis CNC Machining | 4-Axis CNC Machining | 5-Axis CNC Machining |
| Primary Movement | 3 Linear Axes (X, Y, Z) | 3 Linear Axes + 1 Rotation | 3 Linear Axes + 2 Rotations |
| Part Complexity | Low (Planar, 2.5D) | Medium (Cylindrical, Side Features) | High (Complex Contours, Undercuts) |
| Key Advantage | Cost-Effectiveness | Reduced Setups for Side Work | Single Setup for Complex Geometries |
| Typical Cost | $ | $$ | $$$ |
| Surface Finish | Good on accessible surfaces | Good to Excellent | Superior on all contoured surfaces |
| Ideal For | Brackets, Plates, Enclosures | Gears, Cams, Engraved Cylinders | Impellers, Medical Implants, Molds |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What information should I provide to get an accurate CNC machining quote? To get the most accurate quote for your CNC加工 project, you should provide a 3D CAD file (STEP or IGS formats are common), a 2D drawing specifying tolerances, materials, required quantity, desired surface finish, and any secondary processing notes like anodizing or heat treatment. The more detail you provide, the faster and more precise your quote will be.
2. How does surface finish change between 3, 4, and 5-axis machining? While all machines can produce a good finish, 5-axis machining excels at creating superior finishes on contoured surfaces. It allows the use of shorter, more rigid cutting tools that can be kept perpetually tangent to the part surface, reducing tool vibration and eliminating the “scalloping” effect that can occur with 3-axis ball-end mills on curved faces.
3. What is the difference between CNC milling and CNC turning? The main difference is what moves. In CNC milling (which we’ve discussed), the cutting tool rotates and moves to cut a stationary workpiece. In CNC turning, the workpiece rotates at high speed while a stationary cutting tool removes material. Turning is used to create cylindrical or conical parts, like shafts and pins.
Your Partner in Precision CNC Machining
Choosing between 3, 4, and 5-axis CNC machining doesn’t have to be a challenge. By analyzing your part’s design, budget, and timeline, you can confidently select the process that delivers the best value. From the cost-effective simplicity of 3-axis work to the unparalleled capability of 5-axis machining, the right technology is key to your success.
At ly-machining, we are experts in the full spectrum of CNC milling services. Our team is ready to help you navigate these choices and deliver high-quality, precision parts every time. Contact us today to discuss your project and receive a free quote.