Is your brass failing before its time? Unseen factors like brass melting point variances and insidious oxidation could be costing you more than you think. These critical elements often determine component longevity and overall system reliability.
Discover how mastering brass’s core physical properties can unlock unparalleled performance and durability for your critical CNC brass components. We translate complex material science into predictable, high-performing parts.

Rigorous control over brass melting point and effective brass oxidation prevention are fundamental to achieving superior, long-lasting CNC brass components.
Unlock Brass Potential
Setting the Stage & Posing the Question
The performance of CNC brass components is not merely a function of initial design and machining. The intrinsic brass physical properties, particularly its melting point and susceptibility to oxidation, play a decisive role in its long-term viability.
Ignoring these fundamental material characteristics can lead to premature failure and significant unforeseen costs. Engineers and procurement managers must ask: are we truly maximizing our brass potential?
The Hidden Costs of Poor Brass Management
Inadequate attention to brass melting point during machining can introduce internal stresses or microstructural changes, compromising component integrity. This often manifests as reduced strength or increased wear over time.
Similarly, insufficient brass oxidation prevention leads to surface degradation, impacting electrical conductivity, aesthetic appeal, and ultimately, functional lifespan. These failures accrue significant hidden costs in warranties, replacements, and reputational damage.
Why Brass Properties are Critical Now
Today’s advanced applications demand materials that perform consistently under diverse and often challenging environmental conditions. The precise control of brass physical properties has never been more vital.
From aerospace connectors to medical devices, the reliability of CNC brass components hinges on a deep understanding of how these properties influence real-world performance. This technical mastery ensures predictable outcomes.

Core Thesis & Content Preview
Your Blueprint for Superior Brass Parts
This article outlines the essential technical considerations for ensuring optimal performance from brass. It serves as a blueprint for identifying potential pitfalls and implementing robust solutions.
We will explore how precise management of brass’s inherent characteristics directly translates into superior quality and longevity for critical components. Our expertise offers a tangible competitive advantage.
Exploring Key Insights: Melting & Oxidation
We will delve into the scientific principles behind brass melting point and the mechanisms of brass oxidation. Understanding these phenomena is the first step toward effective mitigation and control.
Our discussion will provide practical strategies and insights for engineers seeking to elevate the performance and reliability of their CNC brass components. This knowledge is crucial for informed material selection and process optimization.
Brass Science
Concept & Theory Deep Dive
Brass Melting Point Defined
The brass melting point is not a single fixed temperature but rather a range, typically between 880°C and 920°C (1616°F to 1688°F), depending on the specific alloy composition. This range is due to brass being an alloy of copper and zinc.
Understanding this range is critical for machining, as localized heating during cutting can approach these temperatures, potentially altering the microstructure and affecting material properties.
Understanding Oxidation in Brass
Brass oxidation is a chemical reaction where oxygen in the environment reacts with the copper and zinc on the brass surface, forming oxides. This process creates a dull, often green or black patina.
This surface layer can impair electrical conductivity, alter dimensional stability in precision parts, and reduce the aesthetic appeal of the component. It is a significant concern for long-term performance.

Relevance & Value to You
Impact on Component Lifespan
The careful management of brass melting point during the manufacturing process directly influences the mechanical integrity of the final CNC brass components. Avoiding micro-cracks or phase changes ensures durability.
Effective brass oxidation prevention safeguards the component’s functional lifespan, preserving its intended properties such as conductivity, corrosion resistance, and dimensional accuracy for extended periods.
Optimize Brass Use
Implementation Steps
Managing Melting Point in Machining
Precision CNC machining of brass requires careful control of cutting speeds, feed rates, and coolant application to dissipate heat effectively. This minimizes thermal stress on the material, preventing localized melting.
Our facilities employ advanced simulation software and real-time temperature monitoring to optimize these parameters. This ensures that the brass melting point is never compromised during the manufacturing process.
Preventing Brass Oxidation Effectively
Several strategies are employed for robust brass oxidation prevention. These include selecting appropriate brass alloys with higher inherent resistance, applying protective coatings, and controlling environmental factors.
Post-machining, processes such as passivation, electroplating, or clear lacquering can create a barrier against oxygen. Storage in controlled humidity environments further reduces the risk of degradation.
Table: Brass Oxidation Prevention Methods
| Method | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Passivation | Chemical treatment to create a protective oxide layer. | Moderate to High |
| Electroplating (Nickel) | Coating with a non-reactive metal for a physical barrier. | High |
| Clear Lacquer/Varnish | Transparent organic coating. | Moderate |
| Controlled Environment | Low humidity, inert gas storage. | High (for storage) |
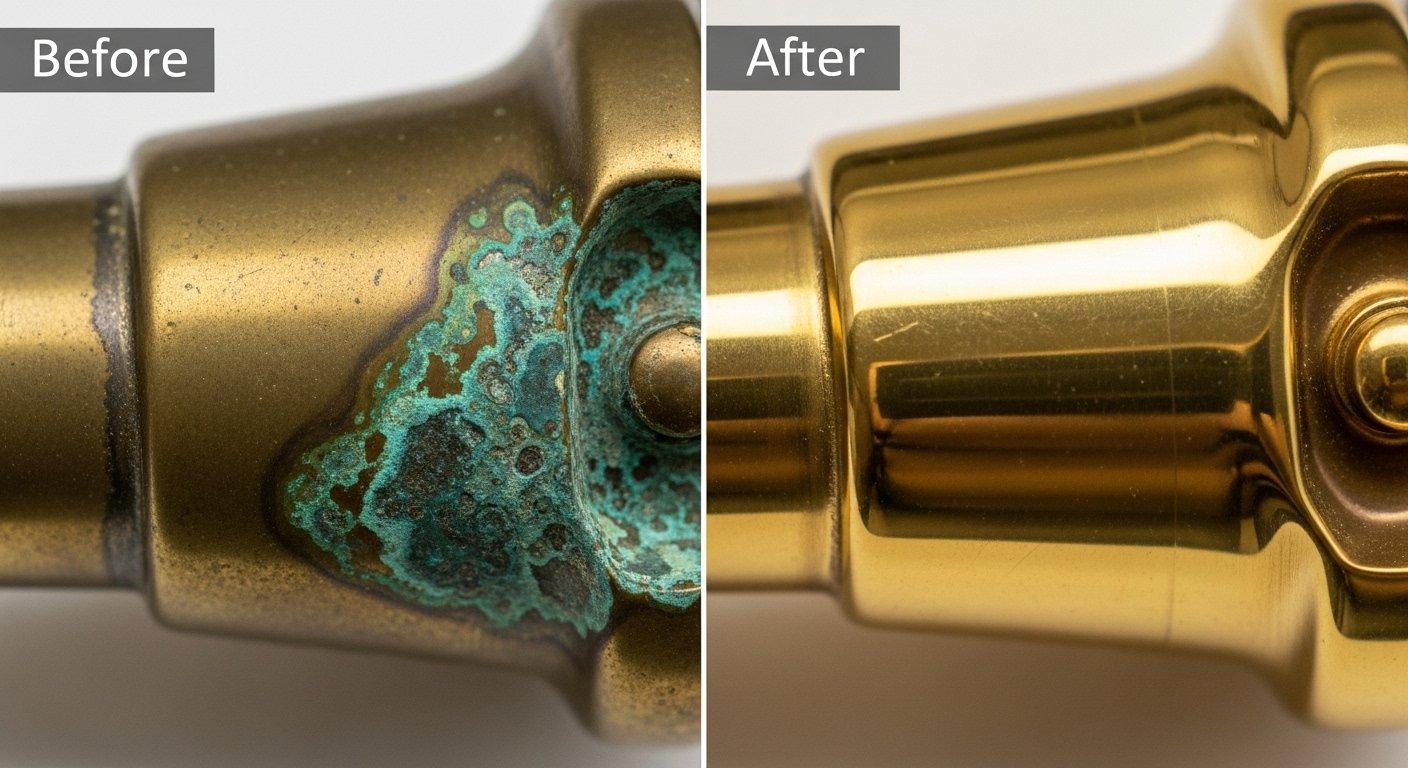

Case Studies & Comparison
Success: Oxidation-Resistant Brass Parts
A client in the marine electronics sector faced consistent failures due to brass oxidation in their navigational sensor housings. Previous suppliers struggled to provide a lasting solution in saltwater environments.
Our solution involved selecting a specialized brass alloy with enhanced corrosion resistance and implementing a multi-layer protective coating system. We also precisely controlled the machining process to maintain the material’s integrity.
The resulting CNC brass components exhibited significantly extended lifespan and performance. This prevented costly field replacements and upheld the client’s reputation for reliability in harsh conditions.
Table: Brass Alloy Oxidation Resistance
| Brass Alloy Type | Typical Composition (Cu/Zn) | Relative Oxidation Resistance | Common Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| C36000 (Free Cut) | 60-63% Cu, 35-38% Zn | Standard | General Machining |
| C27000 (Yellow) | 65% Cu, 35% Zn | Good | Architectural |
| C28000 (Muntz) | 60% Cu, 40% Zn | Moderate | Marine Hardware |
| C46400 (Naval) | 60% Cu, 39% Zn, 1% Sn | Very Good | Saltwater Exposed |
Future-Proof Brass
Overcoming Challenges
Troubleshooting Oxidation Issues
When unexpected oxidation occurs, a systematic approach is essential. This involves analyzing the environment, reviewing the brass alloy used, and scrutinizing post-processing treatments.
Identifying the specific type of oxide and its source is key to implementing a targeted solution. Our engineers can provide forensic analysis to pinpoint issues and recommend corrective measures for brass oxidation prevention.

Advanced Techniques & Trends
Beyond Standard Brass Alloys
The industry is seeing a rise in specialized brass alloys with enhanced properties tailored for specific applications. These include lead-free brass for potable water systems and alloys with improved machinability or corrosion resistance.
Exploring these advanced materials can further optimize brass physical properties for challenging requirements. Our facility stays abreast of these innovations to offer cutting-edge solutions for CNC brass components.
Table: Advanced Brass Alloy Benefits
| Alloy Feature | Benefit | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Free | Environmentally friendly, safe for potable water. | Plumbing fixtures, food contact |
| High Tensile Strength | Enhanced durability under mechanical stress. | Structural components |
| Improved Corrosion Resistance | Superior performance in harsh environments. | Marine, chemical processing |
| Biocompatible | Suitable for medical implants or instruments. | Surgical tools, medical devices |

Act on Brass
Key Takeaways & Reinforcement
Revisit Core Brass Insights
Mastering the brass melting point and implementing robust brass oxidation prevention strategies are non-negotiable for producing high-quality components. These factors directly influence performance and longevity.
A deep technical understanding of brass physical properties allows for informed design, material selection, and manufacturing processes, ensuring superior CNC brass components.
Master Brass Physical Properties
Achieving consistent, high-performance CNC brass components requires a partner with specialized expertise in material science and advanced machining techniques. Our factory embodies this precision.
We are committed to translating complex material characteristics into tangible benefits: reduced risk, extended lifespan, and predictable component performance for your demanding projects.

Call to Action
Partner for Brass Component Excellence
Ready to elevate the performance and longevity of your CNC brass components? Let our engineering expertise guide your next project.
Contact our technical experts today for a free consultation or request a transparent quote for your custom brass machining needs.
FAQ Section
Why is brass melting point important?
Understanding the brass melting point is crucial for precision machining, as excessive heat can alter the material’s microstructure. This can lead to internal stresses, reduced strength, and compromised component integrity. Careful thermal management during machining ensures consistent material properties.
How can I prevent brass oxidation?
Effective brass oxidation prevention involves a combination of material selection and post-processing. Choosing corrosion-resistant brass alloys, applying protective coatings like electroplating or passivation, and storing components in controlled environments are key strategies to mitigate oxidation and preserve surface quality.
What makes ly-machining’s brass unique?
ly-machining excels in producing CNC brass components through rigorous control over brass physical properties. Our expertise in managing brass melting point during machining and implementing advanced brass oxidation prevention techniques ensures unparalleled quality, durability, and precise performance for every part we manufacture.