Rapid Prototyping: CNC vs. 3D Printing
For critical rapid prototyping, CNC machining delivers superior material integrity and precision for functional parts, while 3D printing excels in quick, low-fidelity form validation. The optimal choice hinges on project requirements.
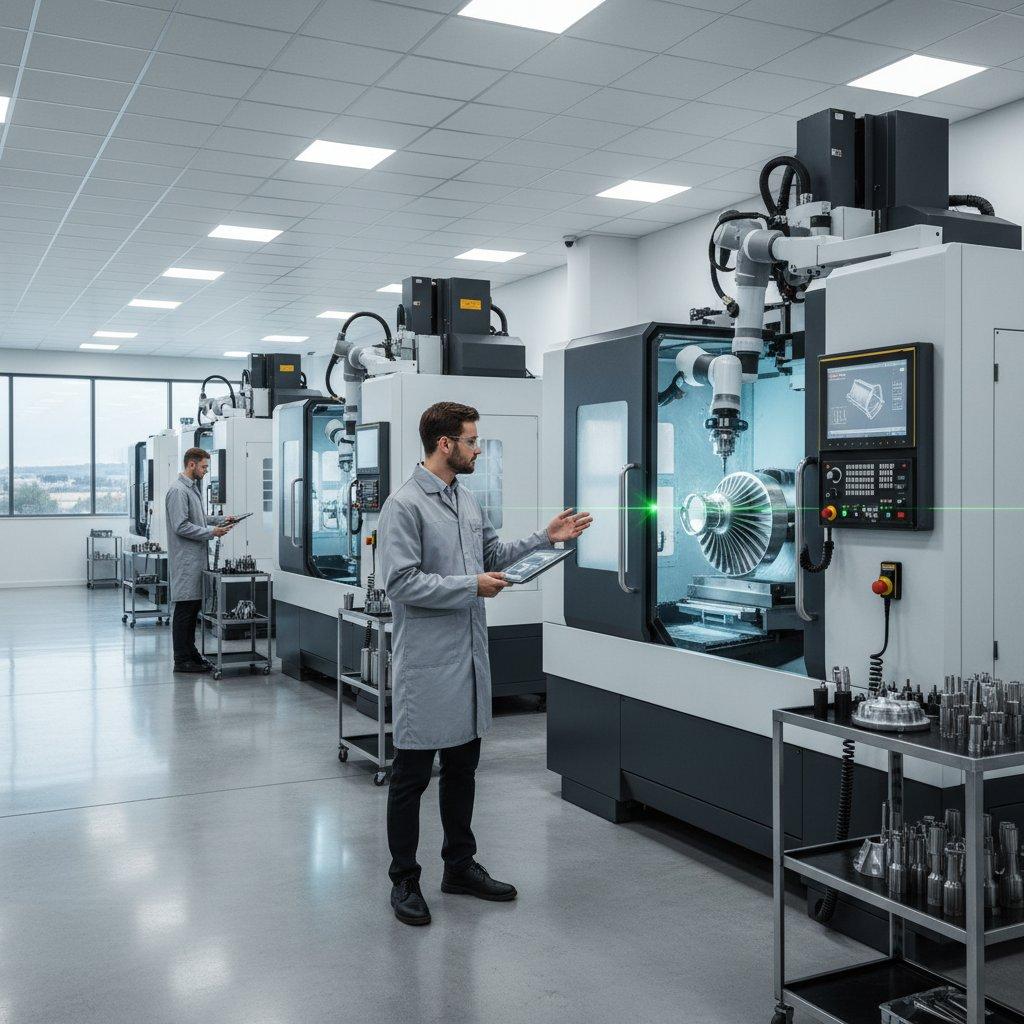
In the fast-paced world of product development, the method of rapid prototyping can significantly impact a project’s timeline, budget, and ultimate success. Engineers and designers frequently weigh the merits of CNC machining prototypes against the flexibility of 3D printing. This choice, however, is far more nuanced than simple speed.
At ly-machining, we understand these complexities from years of hands-on experience in precision manufacturing. Our goal is to illuminate the three fundamental distinctions that differentiate these powerful technologies. We will help you navigate this critical decision, ensuring your project leverages the right approach for optimal outcomes.

Key Differences in Materials & Performance
CNC Prototyping Material Versatility & Strength
In our experience, one of the most significant advantages of Rapid Prototyping CNC is its unparalleled material versatility. CNC machining processes allow for the use of actual production-grade materials, including a wide array of metals like aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and various engineering plastics such as ABS, Nylon, PEEK, and Delrin.
This means that CNC machined prototypes exhibit identical mechanical properties, thermal resistance, and chemical compatibility to their final production counterparts. For functional testing, stress analysis, or validating complex assemblies, this material fidelity is indispensable. We consistently advise clients seeking true performance validation to opt for CNC.
3D Printing Material Options & Limitations
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, offers a diverse range of polymer-based materials, some ceramics, and increasingly, metal powders. While these materials continue to advance, they often do not fully replicate the isotropic properties and strength of traditionally manufactured production materials.
A common issue we see is that 3D printed parts, particularly plastics, can exhibit anisotropy due to their layer-by-layer construction. This can lead to differing strengths along various axes, which can be problematic for functional prototypes intended for real-world stress.
Impact on Functional Prototype Requirements
The choice of prototyping technology directly impacts a prototype’s ability to accurately simulate the end product’s performance. For designs requiring specific mechanical strength, heat resistance, or precise electrical conductivity, the material capabilities of CNC machining prototypes are often the only viable solution.
When we consider the critical requirements for a functional prototype, material selection isn’t just a preference; it’s a fundamental engineering decision. This ensures that validation tests are truly representative of the final product’s expected behavior in the field.
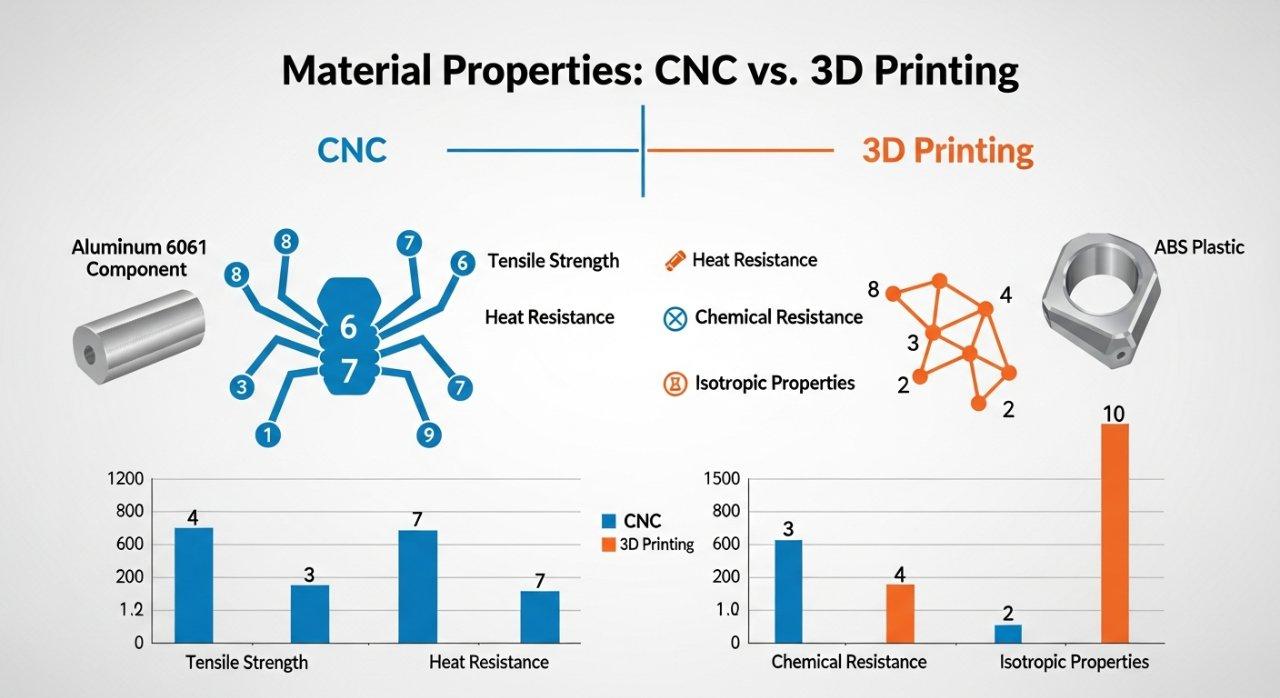
Table: Material Properties Comparison
| Feature | CNC Machining (Metals/Engineering Plastics) | 3D Printing (Plastics/Resins) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Range | Metals (Al, SS, Ti), High-Perf. Plastics | Polymers, Resins, limited Ceramics |
| Isotropic Strength | Excellent (Consistent in all directions) | Variable (Often anisotropic) |
| Thermal Resistance | Generally High | Moderate to High (Material-dep.) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Material-dependent) | Moderate to Excellent (Material-dep.) |
| Electrical Props. | Excellent (Conductive metals, insul. plastics) | Variable (Often insulative) |
Precision & Surface Finish: CNC vs. 3D Print
High Precision & Tight Tolerances with CNC
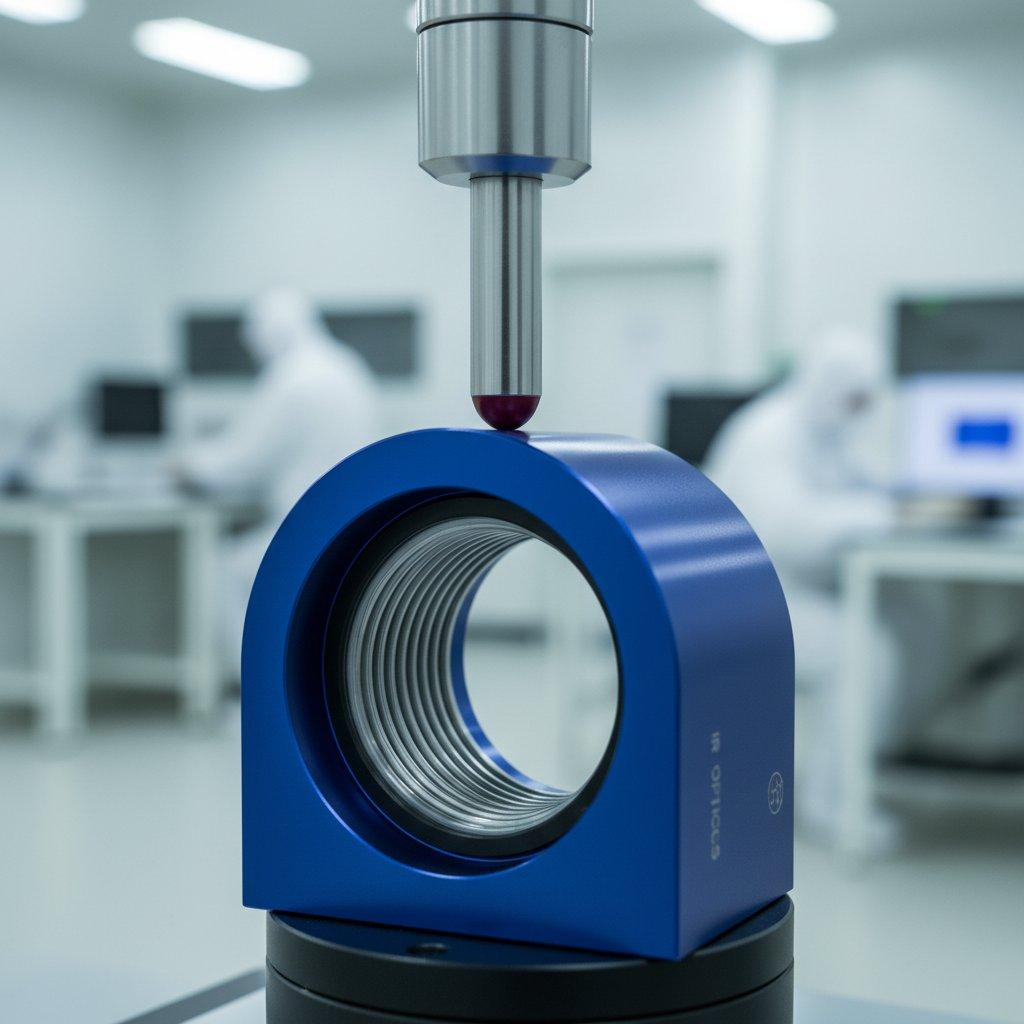
Precision milling and computer numerical control services offer exceptional dimensional accuracy and the ability to hold extremely tight tolerances, often down to ±0.001 inches (±0.025 mm) or even finer. This level of accuracy is critical for parts with complex geometries, intricate features, and assemblies requiring precise fit.
In our manufacturing process, we rely on advanced CNC machines and rigorous quality control protocols to ensure every part meets stringent specifications. This precision is not merely an aesthetic; it’s a functional requirement for components that must interact perfectly within a larger system.

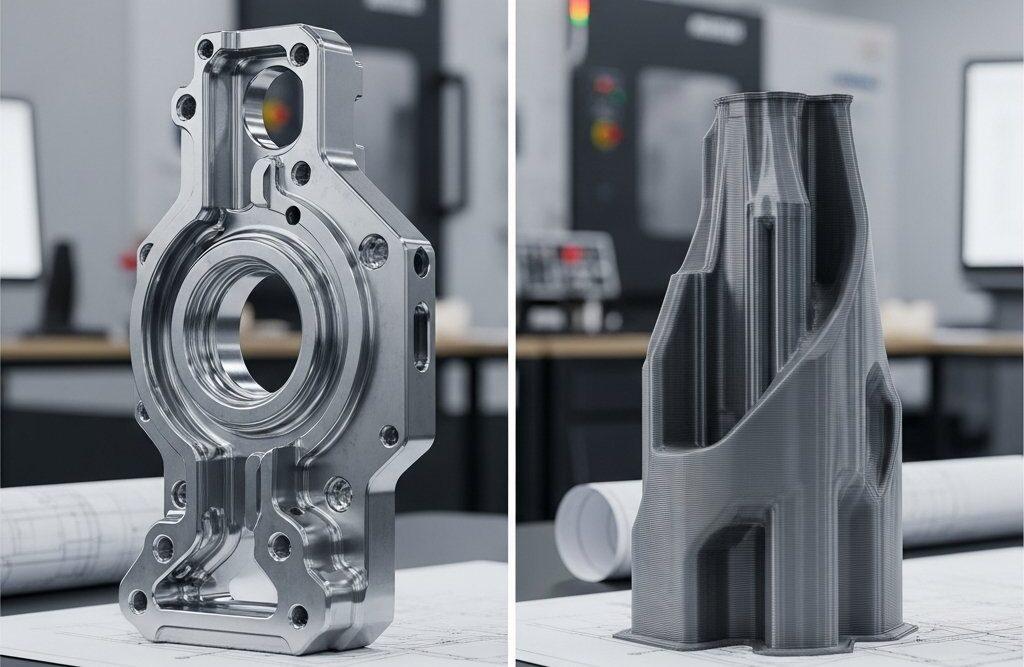
3D Print Layer Lines & Post-Processing Needs
The additive nature of 3D printing inherently creates parts in successive layers. While resolution has significantly improved, microscopic layer lines are typically visible on 3D printed surfaces, impacting both aesthetics and functional performance.
Achieving a smooth, production-quality surface finish on a 3D printed part often necessitates extensive post-processing, including sanding, chemical smoothing, or painting. This adds significant time and cost, potentially negating some of the initial speed advantages, especially for functional prototypes.
Critical for Product Function & Aesthetics
The surface finish and dimensional accuracy are paramount for numerous applications. For example, parts interacting with others via sliding or rotating motion require specific surface roughness to minimize friction and wear. Aesthetics, too, play a vital role in consumer-facing products where perceived quality is crucial.
A superior surface finish achieved directly from CNC machining eliminates the need for labor-intensive secondary operations, ensuring both functional integrity and visual appeal straight off the machine. This directly translates to more reliable prototypes and a smoother transition to final production.
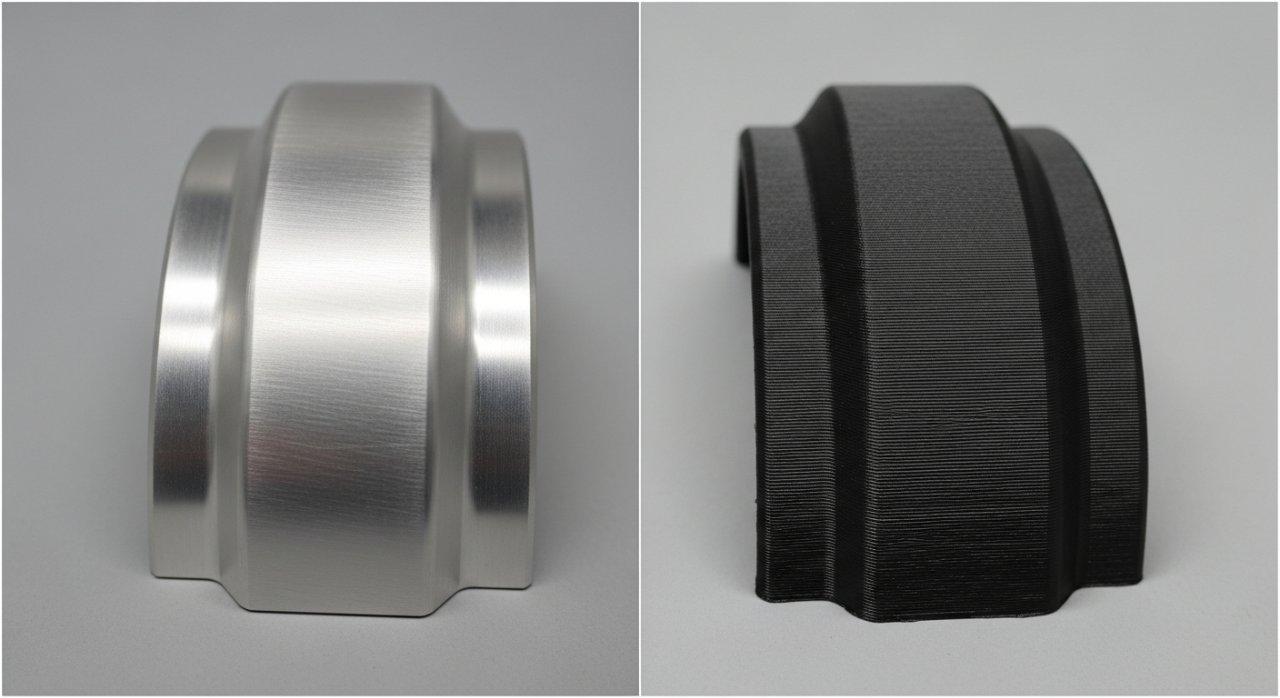

Table: Precision and Surface Finish Comparison
| Feature | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Excellent (±0.001″ or better) | Good to Moderate (±0.005″ to ±0.010″) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, high-quality | Layered, often requires post-processing |
| Geometric Complexity | Excellent (within tool limits) | Excellent (for organic shapes) |
| Feature Detail | Fine, sharp details | Good (can have slight rounding) |
Cost, Speed, & Scalability Differences
Cost Analysis for Single & Small-Batch Prototypes
The cost of rapid prototyping CNC versus 3D printing varies significantly based on part complexity, material, size, and quantity. For single, very intricate plastic parts, 3D printing can be more cost-effective due to minimal setup. However, for multiple units or parts requiring specific materials, CNC machining prototypes quickly become competitive.
In our experience, setup costs for CNC are higher initially, but unit costs drop sharply with increased quantities due to automation and efficient material removal. 3D printing, conversely, often has a more consistent cost per part, regardless of quantity, due to constant material consumption and print time.
Scaling from Prototype to Production with CNC
One of the most compelling advantages of CNC manufacturing for prototyping is its direct scalability to production. The same CAD models and G-code used for a CNC prototype can be directly transferred to large-scale production runs. This seamless transition minimizes design changes and validation cycles.
This “production readiness” aspect of CNC machining prototypes is invaluable. It drastically reduces the risk of “prototype purgatory,” where a 3D printed prototype looks good but fails when an attempt is made to produce it with production methods, leading to costly redesigns and delays.
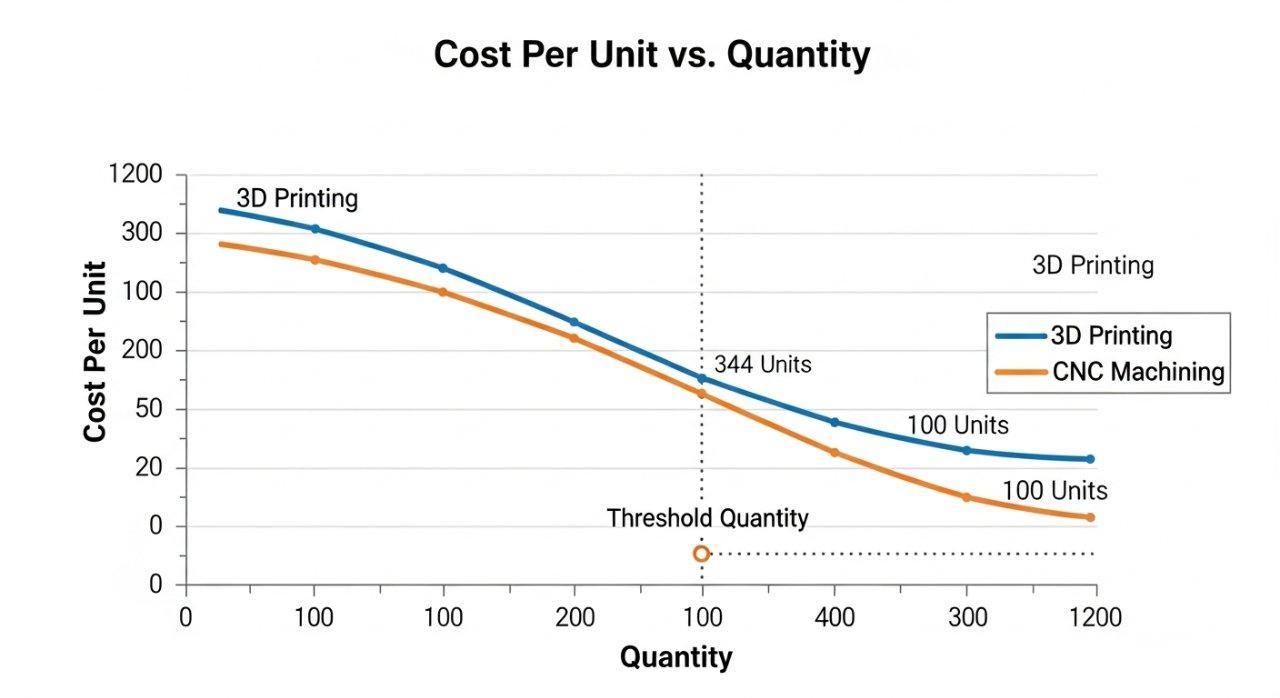
Rapid Iteration & Lead Time Comparison
3D printing generally offers faster initial lead times for simple, low-fidelity prototypes, especially for internal design reviews. A design can be printed overnight. However, factoring in post-processing for better finish and potential material limitations, its true “time-to-functional-prototype” can extend.
CNC machining, while requiring some initial setup, provides remarkably fast turnaround for high-quality, functional prototypes. We often deliver complex CNC machined prototypes within days, depending on complexity and material availability. This efficiency ensures your project stays on track without compromising quality.

Making the Optimal Choice for Your Project
When to Leverage 3D Printing’s Speed
3D printing excels in the very early stages of product development for quick form and fit validation. It’s ideal for conceptual models, ergonomic testing, and visual prototypes where material properties and surface finish are not critical. Its speed for these applications can accelerate initial design iterations.
If your primary goal is to quickly visualize a shape or test basic assembly without demanding functional performance, 3D printing is an excellent tool. It allows for inexpensive, rapid experimentation with geometries.
Why CNC Excels for High-Fidelity Prototypes
For functional prototypes, rigorous testing, or pre-production parts that must closely mimic the final product, CNC machining is the superior choice. Its ability to work with production-grade materials, achieve tight tolerances, and deliver exceptional surface finishes ensures reliable performance validation.
Choosing CNC for these critical applications minimizes the risk of discovering design flaws late in the development cycle, saving significant time and resources. It ensures that the insights gained from prototyping are genuinely predictive of the final product’s success.
Leveraging Expert Consultation for Success
Navigating the choice between rapid prototyping CNC and 3D printing can be complex. The optimal decision often requires a deep understanding of manufacturing processes, material science, and specific project requirements. Engaging with experienced engineers can provide invaluable insights.
We recommend a thorough consultation to discuss your specific application, material needs, tolerance requirements, and budget. Our team can help you identify the most efficient and effective prototyping strategy for your product’s success.
Partnering with a Source Manufacturer
Our Commitment to High-Quality Parts
At ly-machining, our commitment to delivering high-quality parts is at the core of our operations. We adhere to stringent quality control standards, leveraging advanced metrology and inspection equipment to ensure every CNC machined prototype meets your exact specifications.
Our dedication to precision and excellence means you receive reliable, production-ready prototypes that accurately represent your final product. We take pride in being a trusted partner in your product development journey.

Transparent Pricing & Technical Expertise
We believe in complete transparency throughout the prototyping and production process. Our pricing models are clear, comprehensive, and free of hidden fees. You receive detailed quotes that reflect the true cost of precision manufacturing.
Our team of experienced engineers offers deep technical expertise, providing unbiased advice to help you optimize your designs for manufacturability (DFM) and select the best rapid prototyping method. This ensures cost-efficiency without compromising on quality or performance.

**Case Study: Optimizing a Sensor Housing for Harsh Environments**
Problem: A client developing a new environmental sensor required a prototype housing that could withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive chemicals while maintaining strict internal alignment for optical components. Their initial 3D printed plastic prototypes failed heat and chemical resistance tests, deforming and compromising sensor accuracy.
Our Solution: Our engineering team recommended rapid prototyping CNC machining from 316L stainless steel, known for its superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability. We collaborated closely on design for manufacturability (DFM), optimizing wall thicknesses and ensuring tight tolerances for critical mounting features.
Result: The CNC machined prototypes not only passed all environmental and functional tests with flying colors but also provided the necessary precision for optical alignment. This allowed the client to move confidently into small-batch production, saving significant time and resources by avoiding further iterative failures.
Ready for Precision Prototyping?
Contact Us for a Consultation & Quote
Still debating the best prototyping method for your next critical project? Don’t leave precision, material integrity, or production readiness to chance. Contact our expert engineering team today for a transparent quote and an in-depth consultation. Let our deep technical expertise guide you to the optimal rapid prototyping solution, ensuring high-quality parts from a trusted source manufacturer.
**Frequently Asked Questions**
Which method is faster for prototypes?
3D printing offers speed for initial, low-fidelity models. However, for functional prototypes requiring specific materials, precision, and surface finish, the overall time to a usable, test-ready part is often comparable or even faster with CNC machining, especially considering post-processing.
Can CNC prototypes be used for production?
Absolutely. CNC machined prototypes are often made from production-grade materials and utilize the same manufacturing processes as final parts. This makes them ideal for pre-production runs and testing, ensuring a seamless transition to full-scale manufacturing.
What material offers the best performance?
The “best” material depends entirely on your application. CNC machining allows for a vast array of metals and high-performance engineering plastics, offering superior mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties that 3D printing materials often cannot match for critical functional requirements.