Guide to Common CNC Machining Materials
Choosing the right material for your CNC machined part isn’t just a technical decision – it’s a strategic one that defines performance, longevity, and cost. Are you confident your current material choice is truly optimal? Discover how understanding common CNC materials can elevate your product and avoid costly mistakes.

CNC machining materials are diverse, each offering unique properties that impact a part’s function, durability, and manufacturing cost. Selecting the optimal material is crucial for achieving desired performance characteristics, ensuring manufacturability, and staying within budget for any precision component.
Metals for CNC Machining
Metals are foundational to CNC machining, valued for their strength, durability, and versatility. From lightweight aluminum to robust steel, each metal type offers a distinct set of properties for various industrial and consumer applications. Understanding these differences is key to successful product development.
Aluminum Alloys: Optimal for Lightweight CNC Parts
Aluminum alloys are among the most popular choices for CNC machining due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good machinability, and corrosion resistance. They are ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, heat dissipation, and aesthetic finishes. Various grades offer different performance characteristics.
Aluminum alloys are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and consumer product industries. They allow for intricate designs while maintaining structural integrity. Our factory frequently machines complex aluminum parts with tight tolerances.
Here are some common aluminum alloys and their general characteristics:
| Aluminum Alloy Grade | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 6061 | Good strength, weldability, corrosion resistance, common | General purpose, structural components, frames |
| 7075 | High strength, good fatigue resistance, not easily welded | Aerospace parts, high-stress components, molds |
| 5052 | Excellent corrosion resistance, good formability, medium strength | Marine applications, fuel tanks, electronic chassis |
| 2024 | High strength, good fatigue properties, poor corrosion resistance | Aircraft structures, fasteners |
Stainless Steel: Corrosion-Resistant, High-Strength CNC Material
Stainless steel is highly prized for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and aesthetic appeal. It is commonly specified for parts that will be exposed to harsh environments, require frequent sterilization, or need a durable, non-reactive surface.
Several grades exist, each with specific properties regarding hardness, machinability, and resistance to various forms of corrosion. Austenitic grades like 303 and 304 are highly machinable, while martensitic grades offer higher hardness.
Common stainless steel grades and their attributes:
| Stainless Steel Grade | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 303 | Excellent machinability, good corrosion resistance, non-magnetic | Nuts, bolts, shafts, fittings (where machinability is key) |
| 304 | Very good corrosion resistance, excellent weldability, widely used | Kitchen equipment, chemical containers, architectural panels |
| 316 | Superior corrosion resistance (especially to chlorides), higher strength | Marine hardware, medical implants, pharmaceutical equipment |
| 17-4 PH | High strength, hardness, good corrosion resistance, heat treatable | Aerospace components, turbine blades, valve parts |
Copper Alloys: Conductive, Thermally Efficient CNC Applications
Copper alloys, including brass and bronze, are valued for their excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. They also offer good corrosion resistance and are often chosen for their aesthetic properties, especially in decorative or electrical applications.
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is highly machinable and often used for precision fittings and connectors. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, provides higher strength and wear resistance.
Key characteristics of common copper alloys:
| Copper Alloy Type | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Brass (e.g., C36000) | Excellent machinability, good electrical/thermal conductivity, corrosion resistant | Electrical connectors, plumbing fittings, decorative items |
| Bronze (e.g., C93200) | Good strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, excellent bearing properties | Bearings, bushings, gears, marine components |
| Pure Copper (e.g., C11000) | Exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, good ductility | Electrical contacts, heat sinks, busbars |
Titanium Alloys: Challenges for High-End CNC Parts
Titanium alloys are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, outstanding corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. These properties make them indispensable for high-performance applications in aerospace, medical, and marine industries.
However, titanium is significantly more challenging to machine than other metals due to its high strength, low thermal conductivity, and tendency to work harden. This requires specialized tooling, slower cutting speeds, and expert machining techniques.
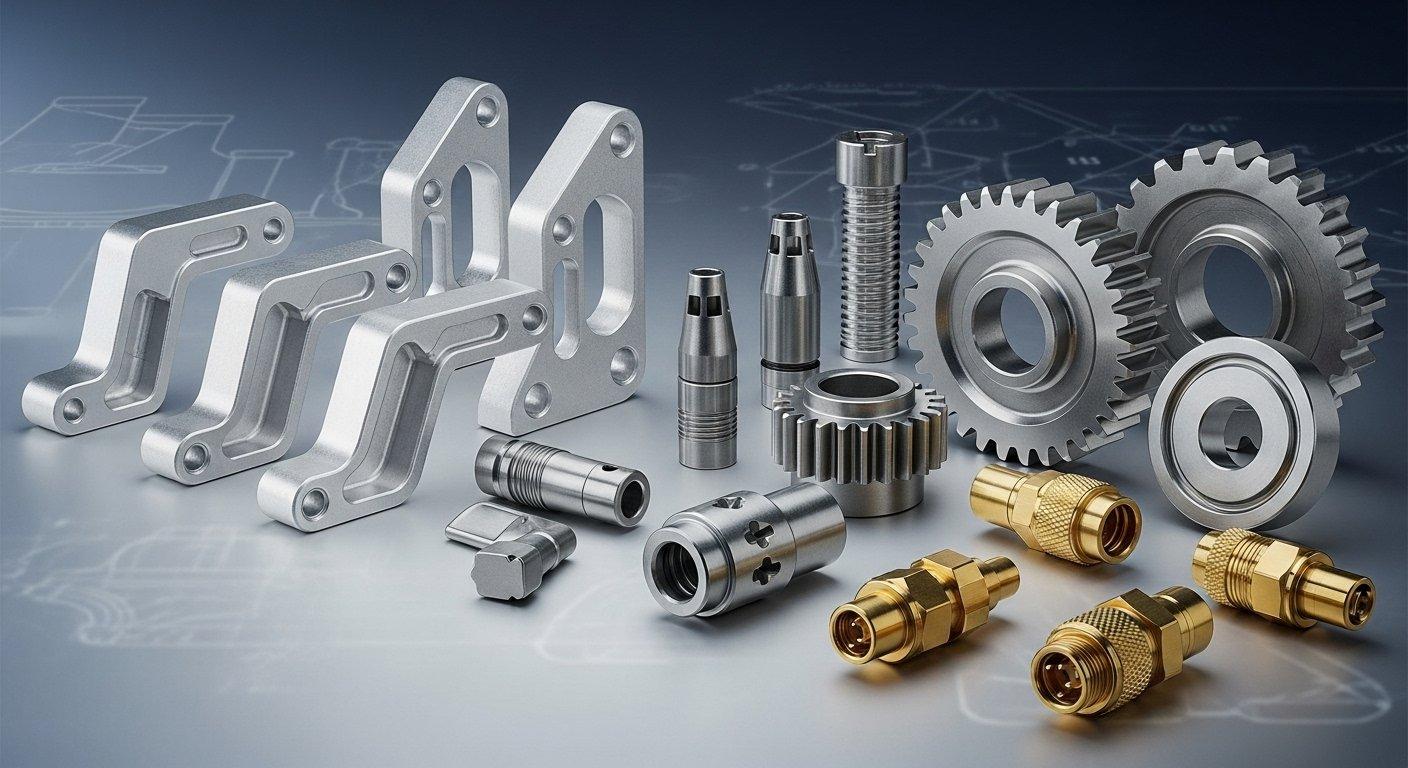

Various Steels: Versatile CNC Machining Materials
Beyond stainless steel, a wide range of other steel alloys is frequently used in CNC machining. These materials offer diverse properties, from high tensile strength to excellent hardness and wear resistance, making them suitable for countless industrial applications.
Carbon steels are cost-effective and strong, while alloy steels contain additional elements to enhance specific properties like toughness or hardenability. Tool steels are designed for extreme hardness and abrasion resistance.
Overview of various steel types:
| Steel Type / Grade | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 1018 Carbon Steel | Good strength, ductility, excellent machinability, easily welded | General purpose, shafts, fasteners, low-stress components |
| 4140 Alloy Steel | High strength, toughness, fatigue resistance, heat treatable | Axles, gears, connecting rods, heavy machinery parts |
| A2 Tool Steel | High wear resistance, good toughness, air hardening | Dies, punches, cutting tools, molds |
| D2 Tool Steel | Very high wear resistance, good hardness, retains sharp edge | Shear blades, stamping tools, high-wear industrial components |
Engineering Plastics for CNC Machining
Engineering plastics offer unique advantages over metals, primarily their light weight, electrical insulation, and often lower material cost. They are ideal for applications where weight reduction, chemical resistance, or non-conductive properties are paramount.
ABS Plastic: Balanced Performance for CNC Parts
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a widely used thermoplastic known for its good balance of strength, impact resistance, and machinability. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to process, making it suitable for a broad range of general-purpose applications.
ABS is often chosen for enclosures, prototypes, and non-critical structural components. Its ability to be easily painted or plated also expands its aesthetic applications.
Key characteristics of ABS plastic:
| ABS Property | Value / Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.02 – 1.08 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 35 – 50 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High |
| Machinability | Excellent |
| Applications | Housings, prototypes, consumer goods, toys |
Nylon Material: Wear-Resistant CNC Machining Applications
Nylon, a polyamide, is a robust engineering plastic recognized for its excellent wear resistance, high strength, and good chemical resistance. It is often reinforced with glass fibers to further enhance its mechanical properties.
Nylon is frequently used for parts requiring durability and low friction, such as gears, bearings, and rollers. Its self-lubricating properties make it suitable for dynamic applications.
Nylon’s performance characteristics:
| Nylon Property | Value / Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.13 – 1.15 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 50 – 90 MPa |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good to many chemicals |
| Applications | Gears, bushings, rollers, insulators |
POM Material: High-Precision CNC Mechanical Parts
POM (Polyoxymethylene), also known as Acetal or Delrin, is a high-performance engineering plastic prized for its high stiffness, low friction, excellent dimensional stability, and good machinability. It maintains its properties well in various environments.
POM is a preferred material for precision mechanical components where tight tolerances and consistent performance are critical. It offers a good balance of mechanical properties without being excessively brittle.

Key properties of POM material:
| POM Property | Value / Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.41 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 60 – 70 MPa |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent |
| Coefficient of Friction | Low |
| Applications | Gears, bearings, medical components, snap-fit assemblies |
PC Plastic: Transparent, High-Strength CNC Parts
PC (Polycarbonate) is a strong, transparent thermoplastic known for its outstanding impact strength, high heat resistance, and optical clarity. It is often considered a glass alternative in applications where breakage is a concern.
Polycarbonate is challenging to machine without specialized techniques to maintain optical clarity and prevent stress cracking. However, its unique combination of strength and transparency makes it invaluable.
Properties of PC plastic:
| PC Property | Value / Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.18 – 1.22 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 55 – 75 MPa |
| Impact Strength | Extremely High |
| Transparency | Excellent |
| Applications | Safety guards, lenses, transparent housings, bulletproof glass components |
Special CNC Machining Materials & Applications
Beyond common metals and plastics, some specialized materials are critical for highly demanding or unique applications. These often present greater machining challenges but offer unparalleled performance in specific niches.
Composite Materials: Custom CNC Machining Needs
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) or glass fiber reinforced polymers (GFRP), offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and stiffness. They are ideal for high-performance applications where weight reduction is critical.
Machining composites is complex due to their anisotropic nature and abrasive fibers, which cause rapid tool wear and require specific cutting strategies to prevent delamination. However, they allow for highly customized, high-strength lightweight parts.
Ceramic Materials: Extreme Hardness CNC Machining
Ceramic materials like Alumina (Al2O3) or Zirconia (ZrO2) are characterized by their extreme hardness, high temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and electrical insulation properties. They are used in environments where metals and plastics fail.
CNC machining ceramics, especially after firing, is exceptionally difficult and usually involves grinding with diamond tools. Machining in a “green” (unfired) state is possible but requires subsequent sintering.
How to Select the Best Material for CNC Parts
Choosing the optimal material is a complex decision that significantly impacts the success of your project. It requires a thorough understanding of the part’s functional requirements, the manufacturing process, and overall project constraints.
Balancing Performance, Cost, and Lead Time
Material selection is a constant trade-off between desired performance, material cost, and manufacturing lead time. A high-performance material might offer superior durability but could significantly increase costs and require longer lead times due to machining complexity or limited availability.
It is essential to identify the non-negotiable performance criteria first, then explore materials that meet these while optimizing for cost and lead time. Over-engineering with an unnecessarily expensive material is a common pitfall.
Consider these trade-offs in your material selection process:
| Factor | High Priority (Example) | Low Priority (Example) | Implication on Material Choice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Aerospace bracket | Basic prototype | High-strength alloy vs. ABS |
| Cost | Consumer product casing | Specialized medical device | ABS vs. Titanium |
| Lead Time | Urgent R&D part | Standard production | Readily available vs. Exotic |
| Machinability | Complex intricate part | Simple block | Aluminum vs. Hardened Tool Steel |
Material Impact on CNC Machining Processes
The chosen material dictates many aspects of the CNC machining process, including tooling, cutting speeds, feed rates, and surface finish capabilities. Harder, more abrasive materials require specialized cutting tools and slower processing.
For instance, machining soft aluminum allows for high speeds and feeds, whereas titanium demands specific tool geometries, low speeds, and generous cooling to manage heat and prevent work hardening. This directly affects machining cost and time.
| Material Type | Typical Machinability | Tooling Requirements | Surface Finish Capability | Cost Impact (Machining) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Excellent | Standard HSS or Carbide | Very Good | Low |
| Stainless Steels | Good to Moderate | Carbide, specific geometries | Good | Moderate to High |
| Titanium Alloys | Difficult | Specialized Carbide, cooling | Good | Very High |
| Engineering Plastics | Excellent to Good | HSS, sharp edges | Good to Very Good | Low |
| Ceramics | Extremely Difficult | Diamond grinding (post-firing) | Excellent | Extremely High |
The Role of Experts in CNC Material Selection
Given the complexities, leveraging expert guidance in material selection is invaluable. Our engineering team at ly-machining possesses deep technical expertise in a vast range of materials and their specific machining characteristics.
We can help you navigate the performance, cost, and manufacturability trade-offs. Our objective is to recommend the optimal material that meets your application’s precise requirements, ensuring both part integrity and project efficiency.

Don’t leave your critical material decisions to chance. Leverage our deep technical expertise and transparent pricing. Contact our expert engineering team today for a personalized material consultation and a precise, no-obligation quote for your high-quality CNC parts project. Let’s engineer your success together.
Article Summary:
This guide explored common CNC machining materials, categorizing them into metals, engineering plastics, and specialized materials. It detailed the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications for each. Key considerations for material selection, including balancing performance, cost, and lead time, and the impact of material choice on machining processes, were also discussed. The importance of expert consultation from a manufacturer like ly-machining for optimal material selection was highlighted.
FAQ Section:
Q1: What are the primary factors to consider when choosing a material for CNC machining?
A1: The primary factors are the part’s functional requirements (e.g., strength, corrosion resistance, weight, electrical properties), the overall project budget, and the desired lead time. It’s crucial to balance these, as high-performance materials often come with higher costs and longer machining times. Our engineers can help weigh these factors.
Q2: How does material choice impact the final cost of a CNC machined part?
A2: Material choice significantly impacts cost in several ways: the raw material’s purchase price, its machinability (which affects machining time, tool wear, and labor costs), and any post-processing requirements like heat treatment or special finishes. Selecting a material that is over-engineered for the application can lead to unnecessary expenses.
Q3: Can ly-machining provide guidance on selecting the best material for a specific application?
A3: Absolutely. As an expert CNC machining factory, ly-machining offers comprehensive material consultation services. Our experienced engineering team possesses deep knowledge of various materials and their machining characteristics. We work closely with clients to understand their specific application requirements and recommend the most suitable, cost-effective material to ensure optimal part performance and project success.