Turning a brilliant digital design into a high-precision physical part can seem like a complex, hidden process. You have a perfected CAD file, but the path it takes through CNC machining to become a tangible product often feels unclear, leaving room for error and uncertainty.
This ambiguity can be a major source of friction in manufacturing. It can lead to misaligned expectations, project delays, and components that don’t quite match your original vision. The gap between the precision of your CAD model and the final CNC milling output can feel vast and fraught with risk, undermining the entire project. This is a common challenge in sourcing custom CNC machining services.
This guide is here to illuminate the entire CNC machining workflow. We will break down the journey from concept to creation into seven clear, understandable steps. By demystifying the process, from the initial CAD design to the final delivered part, we empower you to navigate your next CNC milling project with clarity and confidence.
The CNC machining process transforms a CAD model into a finished part in seven key steps: 1. Creating the foundational CAD file. 2. Translating the design with CAM Programming. 3. Preparing the machine with Setup and Calibration. 4. The core CNC milling or turning operation. 5. Ensuring accuracy with In-Process Quality Control. 6. Applying Finishing and Post-Processing touches. 7. Completing a Final Inspection for delivery.
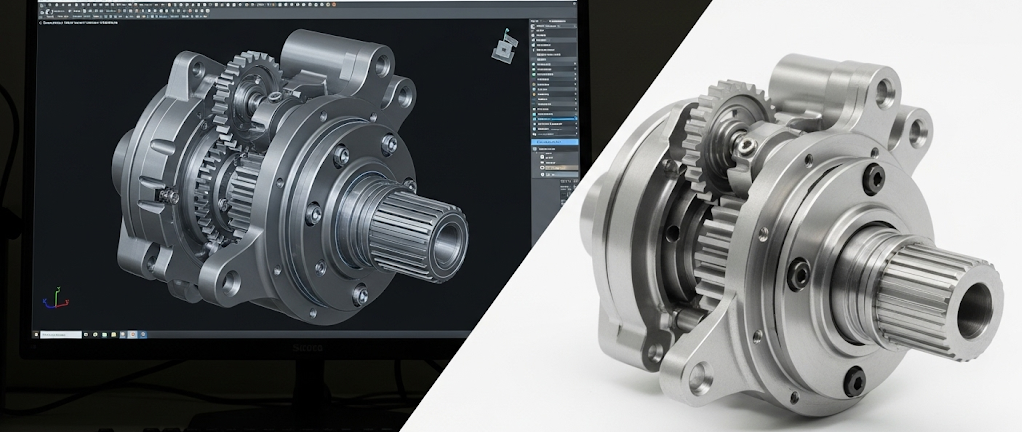
Now that you have this high-level roadmap, it is beneficial to explore each stage in greater detail. Subsequently, a thorough understanding of these steps is essential for anyone involved in product development or sourcing professional CNC machining services. Therefore, let’s begin with the absolute foundation of every successful manufacturing project: the CAD design file. This initial stage is a critical component of the CNC milling workflow.
The Foundation – Crafting the CAD Design File
Everything in precision manufacturing begins with a design. The first step is the creation of a 2D or 3D Computer-Aided Design (CAD) file. This digital blueprint is the single source of truth for the entire CNC machining process, containing all the geometric information required to produce the part. A precise CAD file is paramount.
The quality of the CAD design directly impacts the quality of the final product. It must include not just the shape of the part but also critical information like dimensional tolerances, material specifications, and any notes on surface finishes. A clean, well-defined CAD model ensures that the intent is perfectly translated during the CNC milling stage. This is a non-negotiable part of professional CNC machining.
Common file formats for CNC machining include STEP and IGES for 3D models and DXF or DWG for 2D designs. Providing a comprehensive and accurate CAD file is the most important action you can take to guarantee a successful CNC milling outcome.
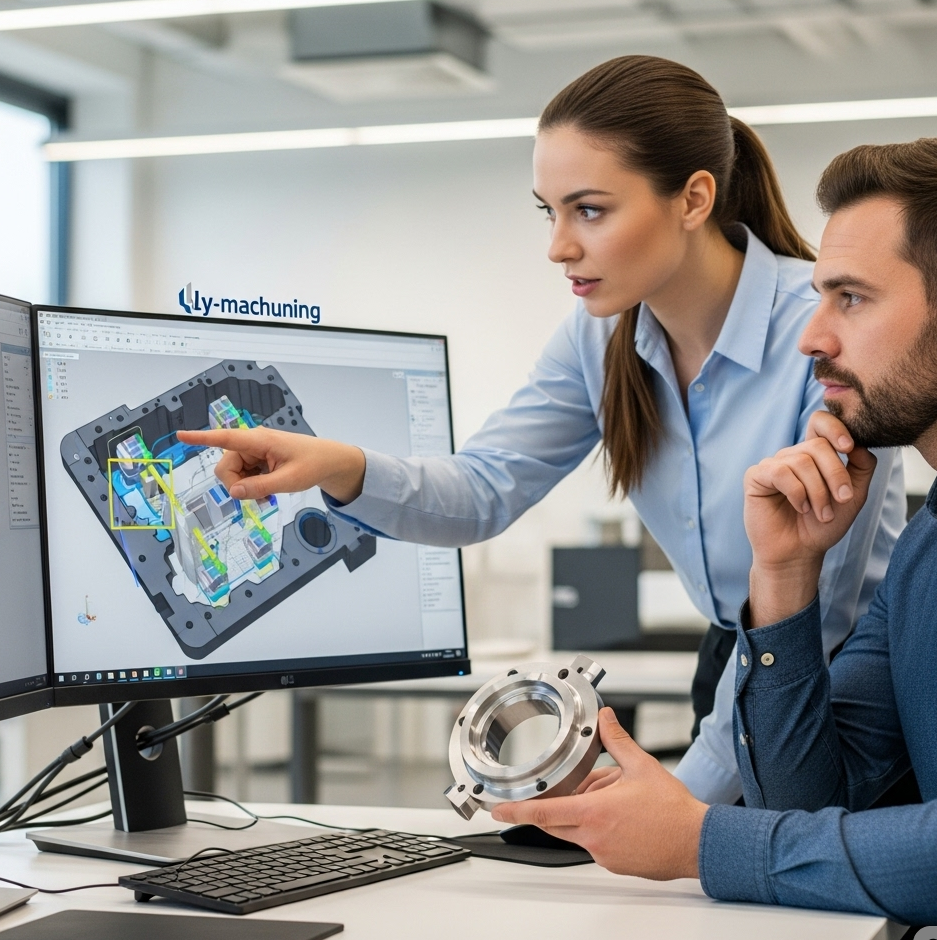
Design to Instruction – CAM Programming
A CNC machine cannot directly read a CAD file. The design must be translated into a specific set of instructions, and this is where Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software comes in. A manufacturing engineer or programmer imports the CAD file into a CAM program to prepare it for CNC machining.
The CAM software is used to generate the toolpaths—the exact route the cutting tool will take to remove material. The programmer will also define crucial parameters like cutting speeds, feed rates, and the sequence of operations. This stage effectively creates the strategy for the CNC milling process. The quality of the CAM programming is as vital as the initial CAD design for efficient CNC machining.
The output of this stage is a file containing machine code, typically G-code and M-code, which is the language the CNC machine understands. This code directs every movement, action, and function of the machine during the CNC milling operation.
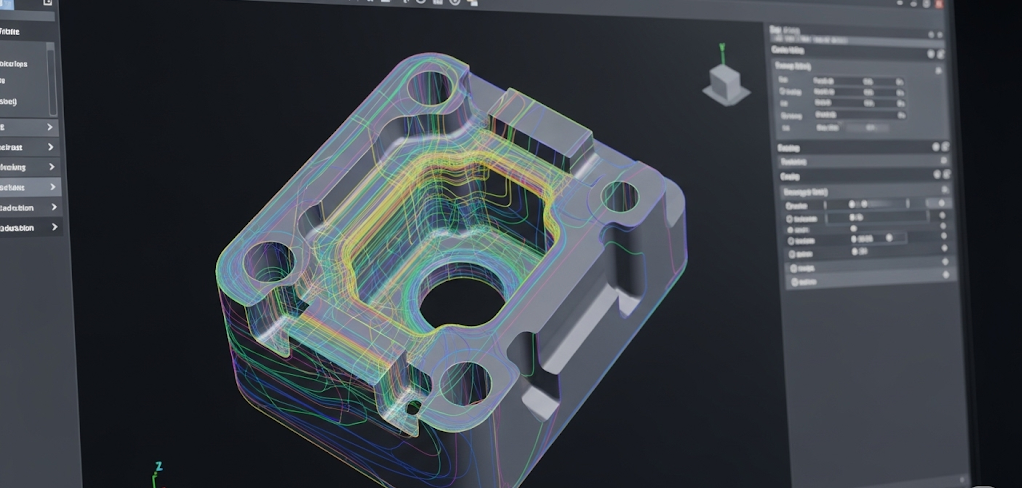
Preparing the Machine – Setup and Calibration
Before any cutting begins, the CNC machine must be meticulously prepared. This setup stage is a hands-on process that requires precision and expertise. A skilled technician ensures that every element is perfectly aligned with the plan derived from the CAD and CAM files. This is a manual, yet critical, part of the CNC machining process.
The process involves several key actions:
- Workpiece Fixturing: The raw block of material (the workpiece) is securely clamped into the machine’s workholding device (a vise or custom fixture). It must be held rigidly to prevent any movement during the powerful CNC milling operation.
- Tool Installation: The correct cutting tools (end mills, drills, etc.) are selected and loaded into the machine’s tool changer. The integrity of these tools is vital for any CNC machining task.
- Setting Offsets: The technician calibrates the machine by setting the zero point or “datum” on the workpiece and measuring the exact length of each tool. This ensures the machine knows the precise location of the workpiece and the tools in relation to the CAD model’s coordinates.
Proper setup is fundamental to achieving the tight tolerances expected from high-quality CNC machining and CNC milling.
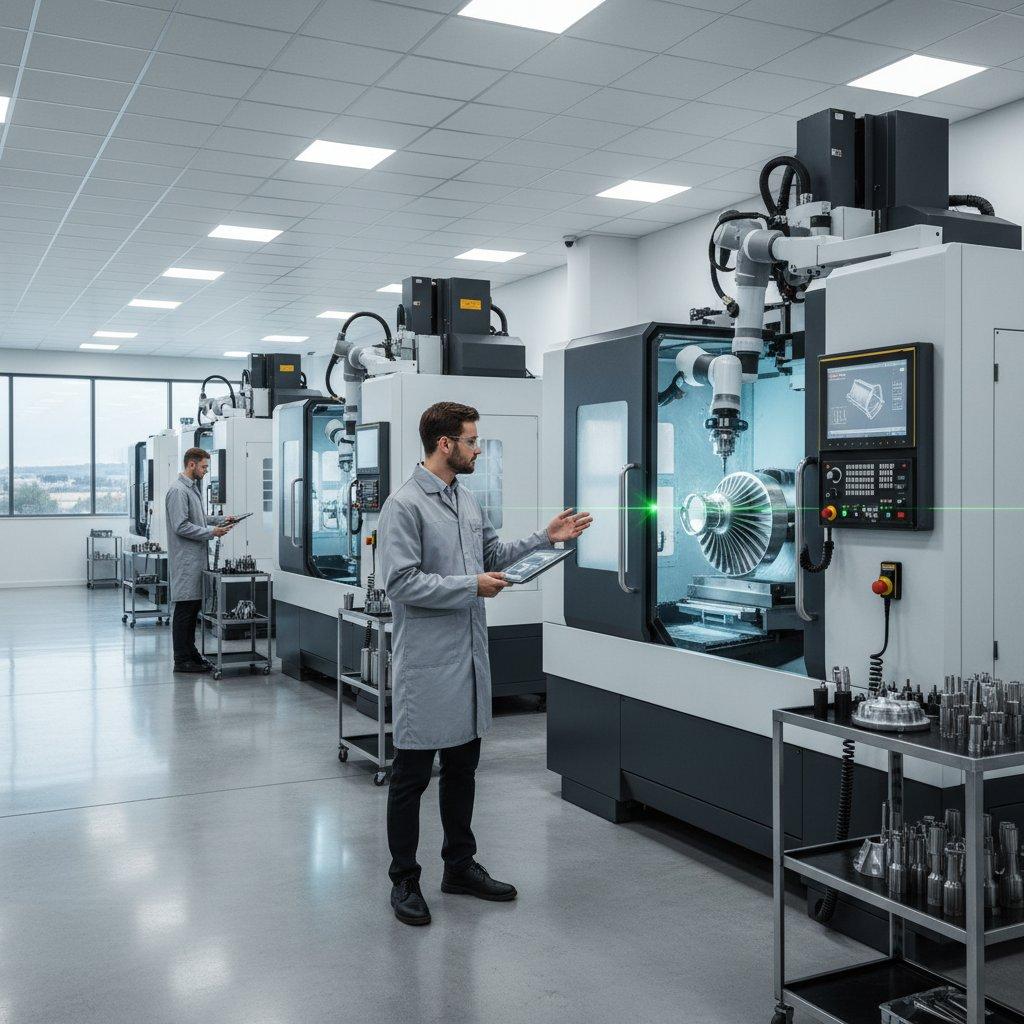
The Main Event – The CNC Machining Operation
With the setup complete, the core manufacturing process can begin. The machine operator loads the G-code file, closes the safety doors, and initiates the cycle. This is where the digital CAD file truly starts to become a physical object through the subtractive CNC machining process.
The CNC machine’s controller reads the G-code line by line, executing each command with incredible speed and precision. The machine autonomously controls the movement of the cutting tools and the workpiece, progressively removing material according to the programmed toolpaths. This is the essence of CNC milling.
Whether it’s a CNC milling machine cutting pockets and contours or a CNC lathe turning a cylindrical profile, this automated process ensures that every part is a perfect replica of the one before it. The efficiency and repeatability of this step are why CNC machining is the standard for producing complex and high-precision components.

Ensuring Accuracy – In-Process Quality Control
Quality is not just checked at the end; it is built into every stage of the CNC machining process. During and between operations, it is common practice to perform in-process quality control. This proactive approach catches any potential deviations early, before they become significant problems. This is a core principle at ly-machining for all CAD-driven projects.
Operators may use a variety of metrology tools, such as digital calipers, micrometers, and height gauges, to check critical dimensions against the specifications laid out in the CAD drawing. For highly complex parts, automated touch probes inside the CNC machine can measure features mid-cycle. This ensures the CNC milling process is proceeding as planned.
This commitment to ongoing inspection is essential for maintaining tight tolerances and ensuring the consistency of every part produced. This is a hallmark of a reliable CNC machining service provider.

The Final Touches – Finishing and Post-Processing
Once the primary CNC machining operations are complete, the part is not yet finished. It then moves to the post-processing stage, where it receives its final cosmetic and functional treatments. This step transforms a raw machined part into a finished product ready for assembly.
Common post-processing steps include:
- Deburring and Cleaning: Manually or automatically removing any small burrs left by the cutting tools and thoroughly cleaning the part to remove cutting fluids and chips.
- Surface Finishing: Applying treatments like sandblasting, anodizing, powder coating, or plating to enhance cosmetic appearance, improve corrosion resistance, or add specific surface properties. This is a key value-add to the core CNC milling service.
This finishing stage is crucial for meeting all the specifications noted in the original CAD file and delivering a professional-grade component. This is an integral part of the complete CNC machining service.
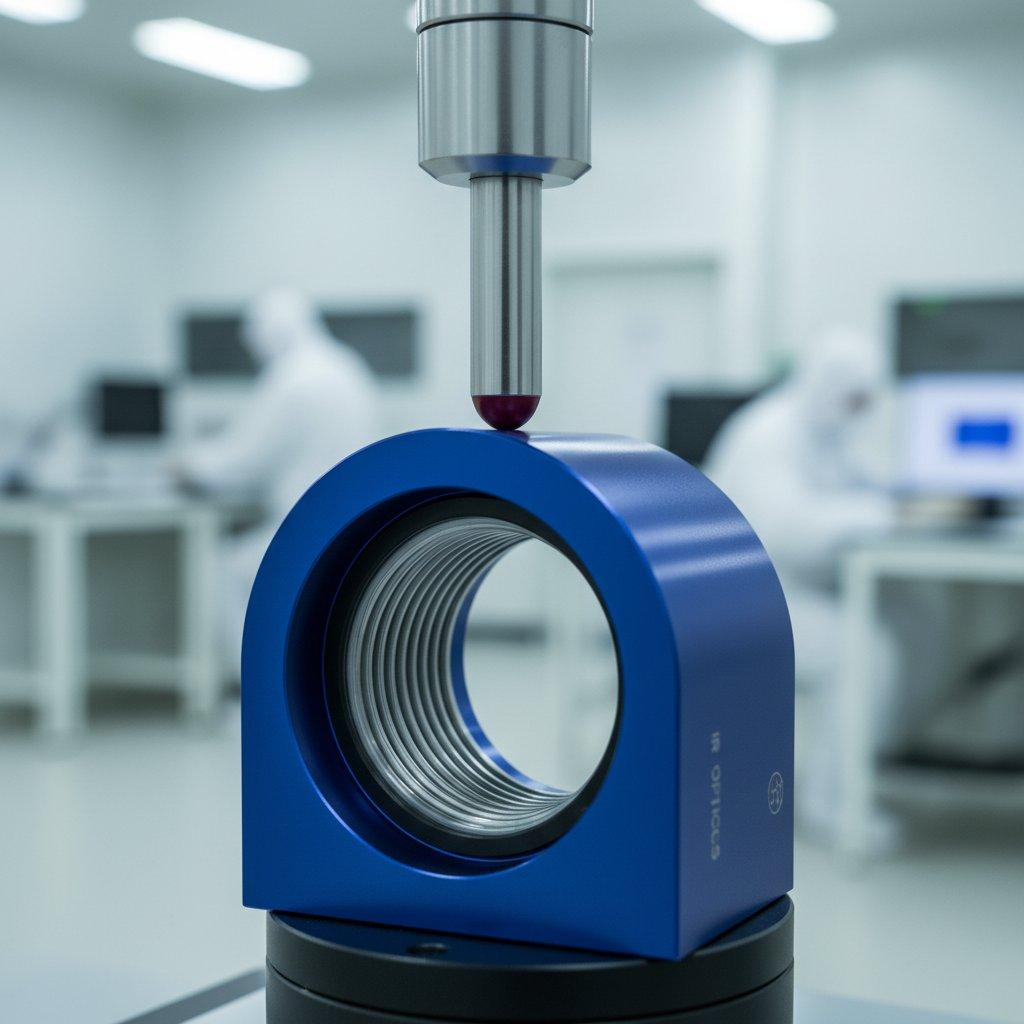
The Finish Line – Final Inspection and Delivery
The final step before the product is shipped is a comprehensive final inspection. This is a gatekeeping process where the finished part is meticulously checked against the original CAD model and engineering drawings one last time. Every feature, dimension, and requirement is verified.
Quality control specialists use advanced metrology equipment, such as a Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM), which can measure parts with extreme accuracy. This ensures that the component adheres perfectly to the specified tolerances. This confirms the success of the entire CNC machining journey, from CAD to final part.
Once a part passes this final inspection, it is carefully packaged to protect it during transit and then delivered to the client. This final step closes the loop, successfully transforming a CAD file into a high-quality component, which is the ultimate goal of any CNC milling project.

Related Questions
What is the difference between CNC Machining and CNC Milling?
This is a common point of confusion. CNC Machining is the broad term for any computer-controlled subtractive manufacturing process. CNC Milling is a specific type of CNC machining that uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from a stationary workpiece. Other types of CNC machining include turning (where the workpiece rotates), drilling, and grinding. So, all CNC milling is CNC machining, but not all CNC machining is CNC milling.
How can I optimize my CAD file for more efficient CNC machining?
To ensure your CAD file is ready for manufacturing, follow a few best practices. Use standard fillet radii to avoid the need for custom tools. Design pockets and cavities with corner radii that are slightly larger than the end mill’s radius to prevent stress concentrations. Ensure all tolerances are clearly defined, but avoid making them unnecessarily tight, as this increases CNC machining time and cost. Providing a clean, optimized CAD file is key to a smooth CNC milling process.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does the entire CNC machining process take from CAD submission?
The lead time for a CNC machining project depends on several factors: the complexity of the part design in the CAD file, the quantity of parts required, the material being used, and the finishing processes needed. A simple prototype might be produced in a few days, while a large production run of complex CNC milling parts could take several weeks. We provide a clear timeline estimate after reviewing your CAD file and requirements.
2. What information do I need to provide besides the CAD file?
While the CAD file is the most critical piece of information, a complete request for a quote (RFQ) should also include the material type (e.g., Aluminum 6061, Stainless Steel 304), the quantity of parts needed, the required surface finish (e.g., anodized, as-machined), and any critical tolerances that must be held. This complete package of information ensures the most accurate pricing and successful CNC machining outcome.
3. How does ly-machining ensure my CAD design intent is perfectly met?
At ly-machining, we conduct a thorough Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis on every CAD file we receive. Our engineers review your design to identify any features that may be difficult or overly expensive to machine. We then proactively communicate these findings and suggest potential optimizations, ensuring the final part from our CNC milling process not only meets your design intent but is also produced efficiently and cost-effectively. This is a core part of our CNC machining philosophy.