The Ultimate Guide to CNC Aluminum Anodizing
Are you tired of inconsistent finishes, unpredictable lead times, and hidden costs undermining your CNC aluminum anodizing projects? These common challenges often lead to costly rejections and significant delays, impacting product integrity and market schedules.
Understanding the intricate anodizing process is paramount for achieving superior results that meet demanding specifications. This guide will reveal the essential technical aspects and best practices to transform your parts into high-performance, visually stunning components.
Discover how meticulous process control, advanced material science, and strategic color selection can ensure reliability, enhance brand identity, and deliver consistent quality in every batch.
Featured Snippet: Mastering CNC aluminum anodizing involves precise control over electrochemical processes, material selection, and post-treatment techniques to achieve superior durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic consistency.

Anodizing: Why It Matters
Industry Challenges & Solutions
Inconsistent quality & project delays
Achieving consistent quality in CNC aluminum anodizing is a persistent challenge for many industries. Variations in surface finish, thickness, and color often lead to costly scrap rates and critical production delays.
These inconsistencies directly impact project timelines and can erode customer trust in product reliability. Precise control over every stage of the anodizing process is essential to mitigate these risks.
The critical role of proper finishing
Proper finishing, specifically anodizing, is not merely aesthetic; it is a fundamental engineering requirement. It significantly enhances the functional performance of aluminum components, extending their lifespan in various operational environments.
Without a meticulously controlled anodizing process, even perfectly CNC machined parts can fail prematurely due to corrosion, wear, or an unacceptable appearance.
What You’ll Learn Today
Mastering CNC aluminum anodizing
This guide provides an in-depth exploration of CNC aluminum anodizing, offering insights into the science and practical application. We aim to equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions for your projects.
Understanding the nuances of each stage is crucial for optimizing outcomes and ensuring your components meet the highest standards.
Process, benefits, and color options
We will comprehensively cover the entire anodizing process, from initial preparation to final sealing. Additionally, we will detail the substantial anodized aluminum benefits, including enhanced durability and diverse color selection.
This technical overview is designed to clarify complex aspects and highlight how our expertise addresses specific client needs.
The Process
The Core Science Explained
Defining anodizing for aluminum
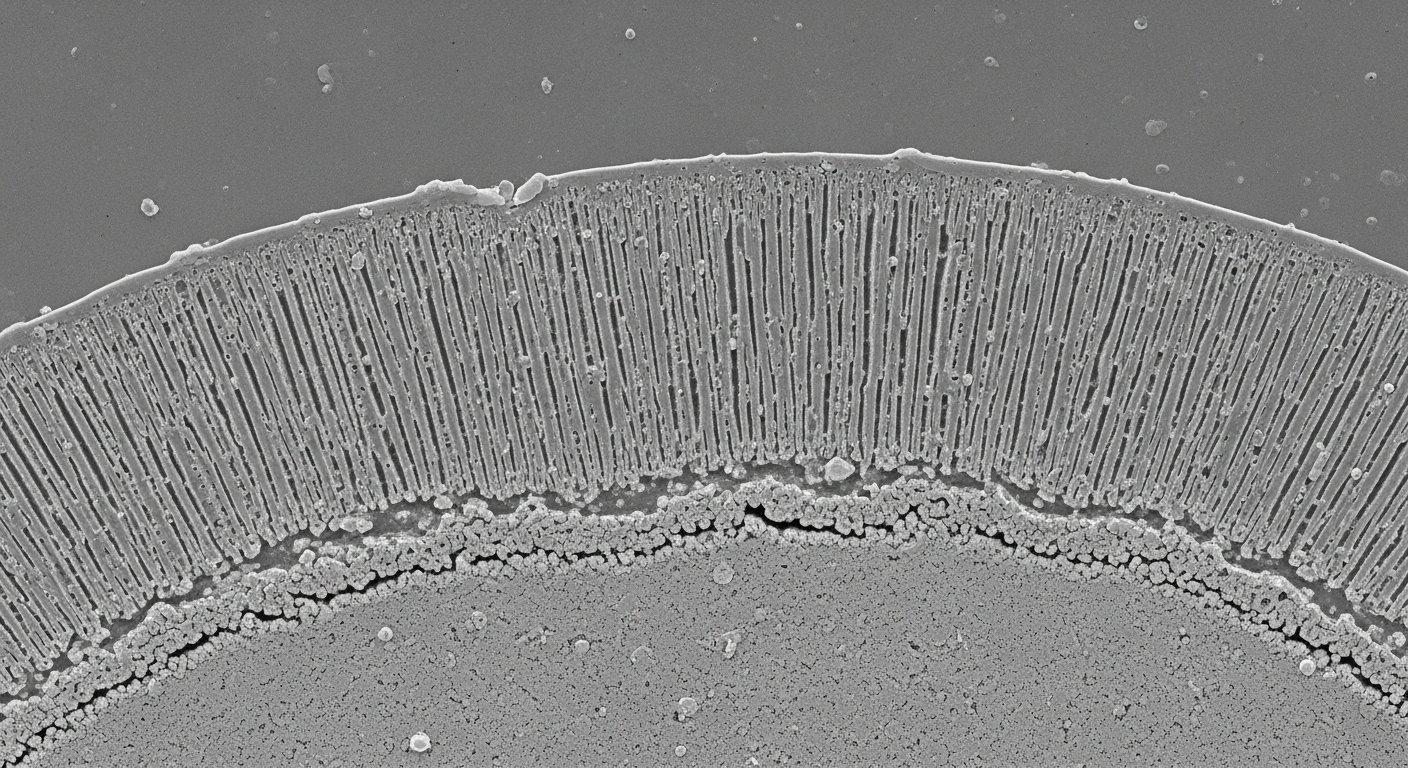
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metallic surface of aluminum into a decorative, durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish. This layer is integral to the aluminum substrate, unlike applied coatings.
The process leverages the natural propensity of aluminum to form an oxide layer, but significantly enhances its thickness and hardness through controlled oxidation.
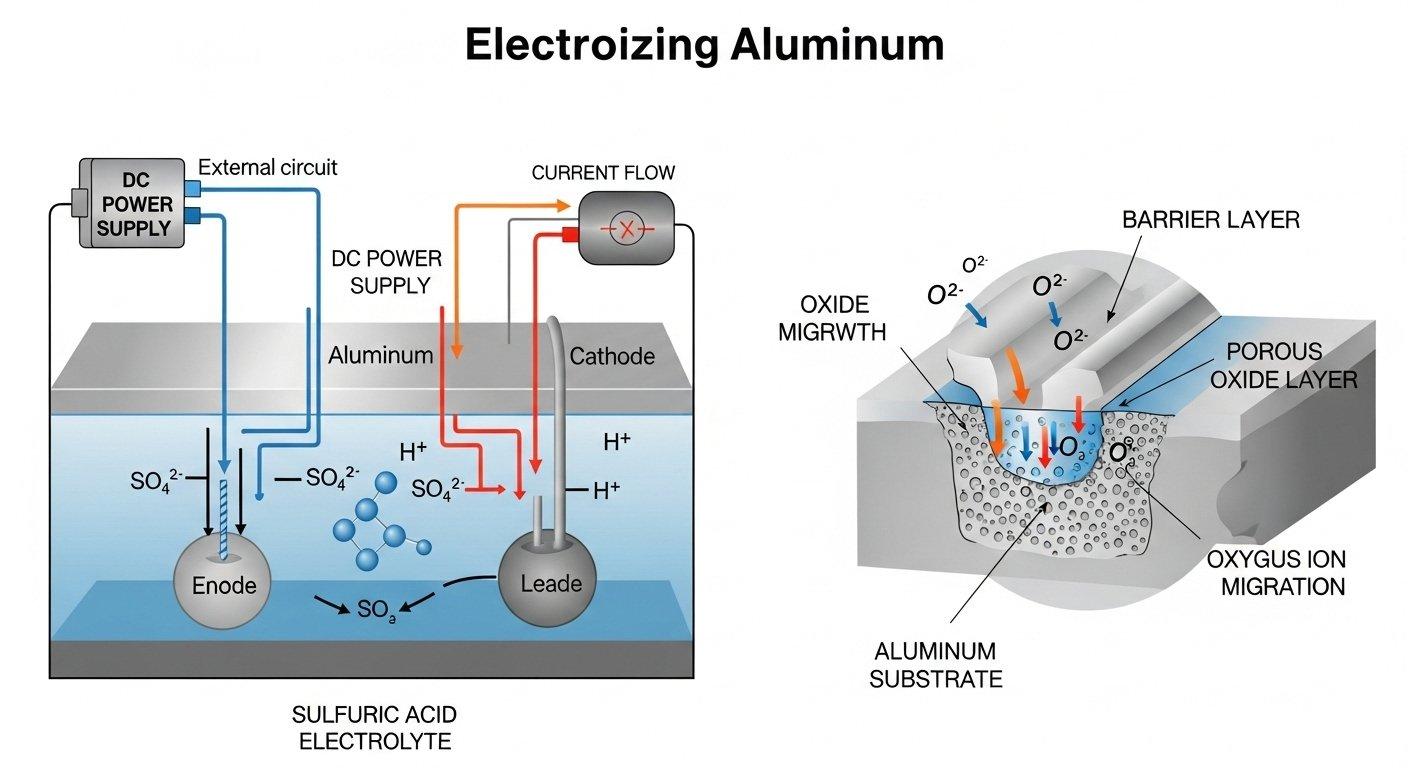
How the electrochemical process works
During the anodizing process, aluminum parts are submerged in an electrolyte bath and an electric current is passed through. The aluminum acts as the anode, causing oxygen ions to combine with aluminum atoms on the surface.
This reaction forms a porous aluminum oxide layer that grows both outwards and inwards from the original surface. The controlled formation of this layer is what imparts the desired properties.
Step-by-Step Implementation
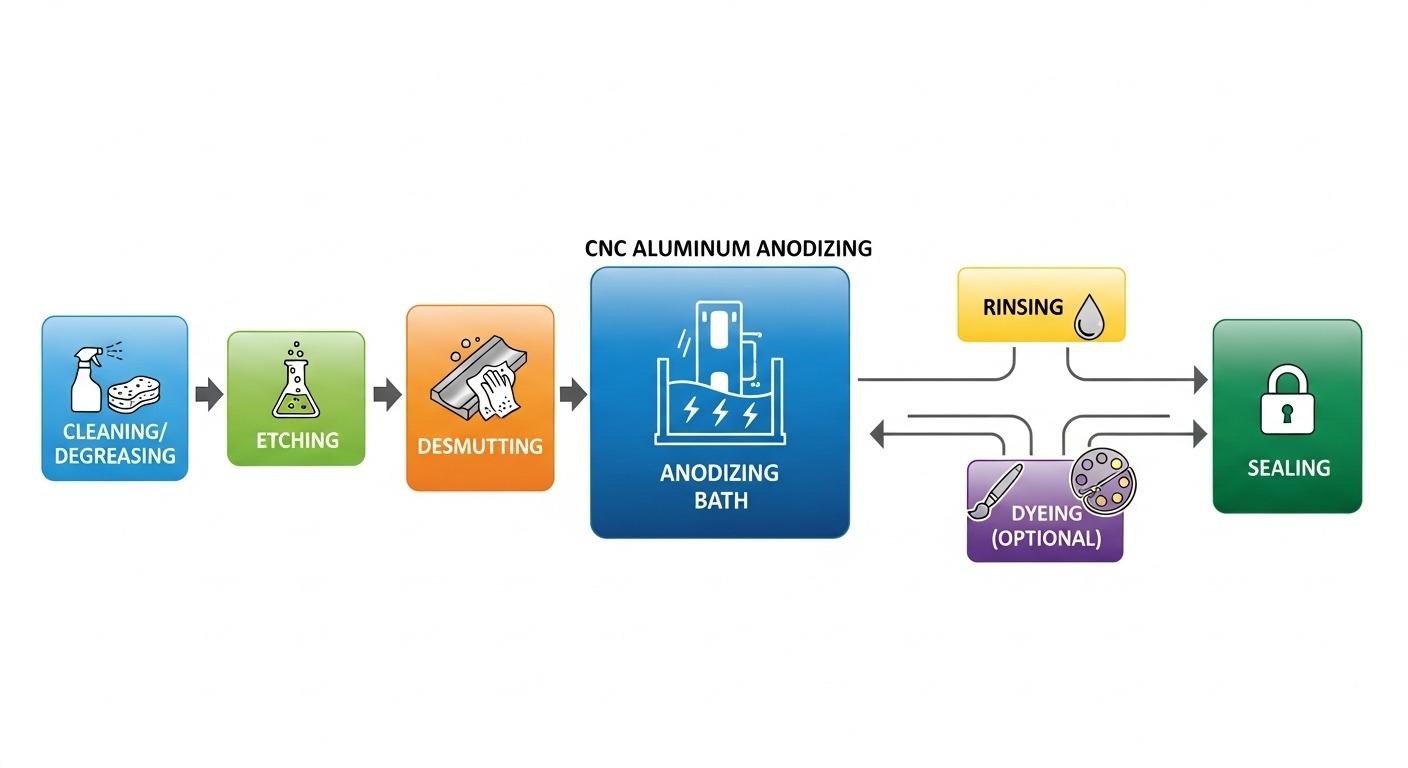
Detailed anodizing sequence
The comprehensive anodizing sequence typically begins with pre-treatment to ensure a pristine surface. This is followed by the electrolytic bath where the oxide layer forms, then rinsing, and often a dyeing stage.
The final, critical step is sealing, which closes the pores in the oxide layer, significantly enhancing corrosion resistance and color retention. Each stage requires precise control for optimal results.
Crucial pre-treatment techniques
Effective pre-treatment is indispensable for successful anodizing. It involves several stages designed to prepare the aluminum surface, ensuring optimal adhesion and consistency of the anodic layer.
These stages typically include alkaline cleaning to remove oils and dirt, etching to create a uniform matte finish and remove minor surface imperfections, and desmutting to eliminate any residual smudges or particles.
Benefits/Colors
Enhancing Performance & Durability
Superior corrosion & wear resistance
One of the primary anodized aluminum benefits is significantly enhanced corrosion resistance. The dense, hard oxide layer acts as an effective barrier against environmental degradation, protecting the underlying aluminum from oxidation and chemical attack.
This robust surface also exhibits superior wear resistance, making anodized components ideal for applications requiring high durability and longevity.
Increased hardness & extended lifespan
The anodic oxide layer is considerably harder than raw aluminum, often approaching the hardness of sapphire for Type III hard coat anodizing. This increased surface hardness dramatically improves resistance to scratches, abrasion, and general wear.
Consequently, anodized parts experience an extended operational lifespan, reducing maintenance requirements and replacement costs.
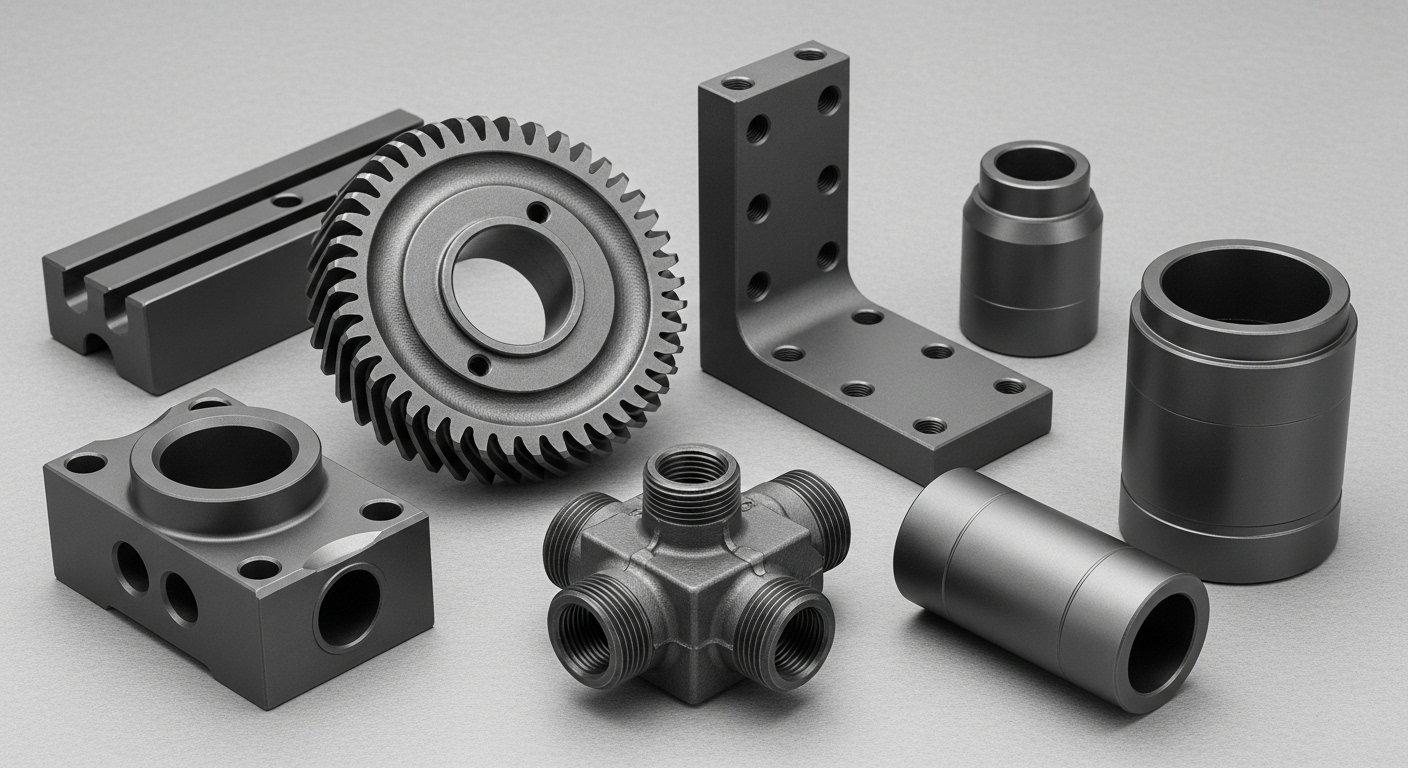

Unlocking Aesthetic Potential
Vast anodizing color selection
The porous nature of the anodic layer before sealing allows for an extensive anodizing color selection. Dyes can be absorbed into these pores, creating a wide spectrum of vibrant and consistent colors that are integral to the surface.
This capability provides product designers with immense flexibility to align component aesthetics with specific brand guidelines or functional requirements.
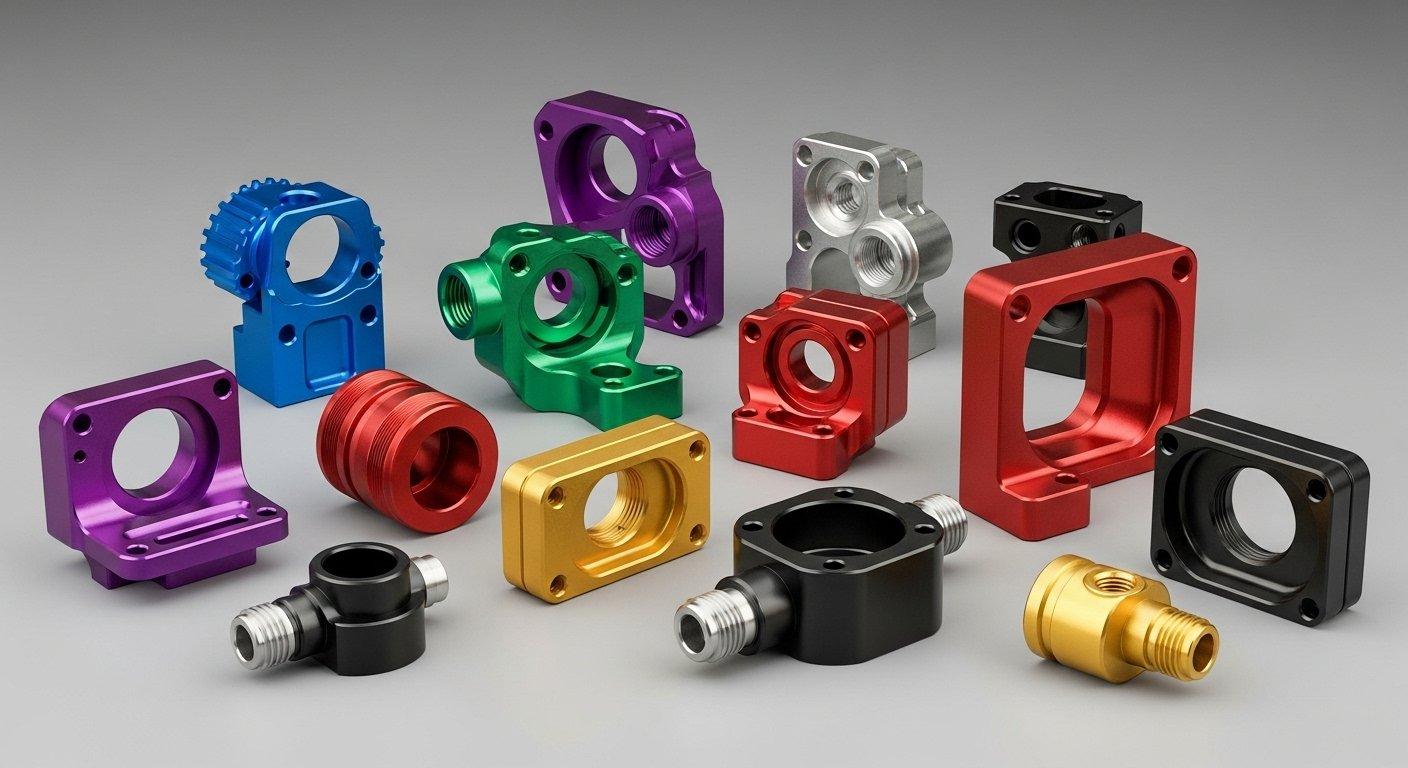

Premium, consistent surface finish
Beyond color, anodizing provides a premium, consistent surface finish that enhances the tactile and visual appeal of aluminum parts. The process can yield various textures, from matte to semi-gloss, depending on pre-treatment and anodizing parameters.
This uniform and high-quality finish is crucial for products where aesthetics and brand perception are key differentiators in the market.
Achieve Quality
Addressing Common Pain Points
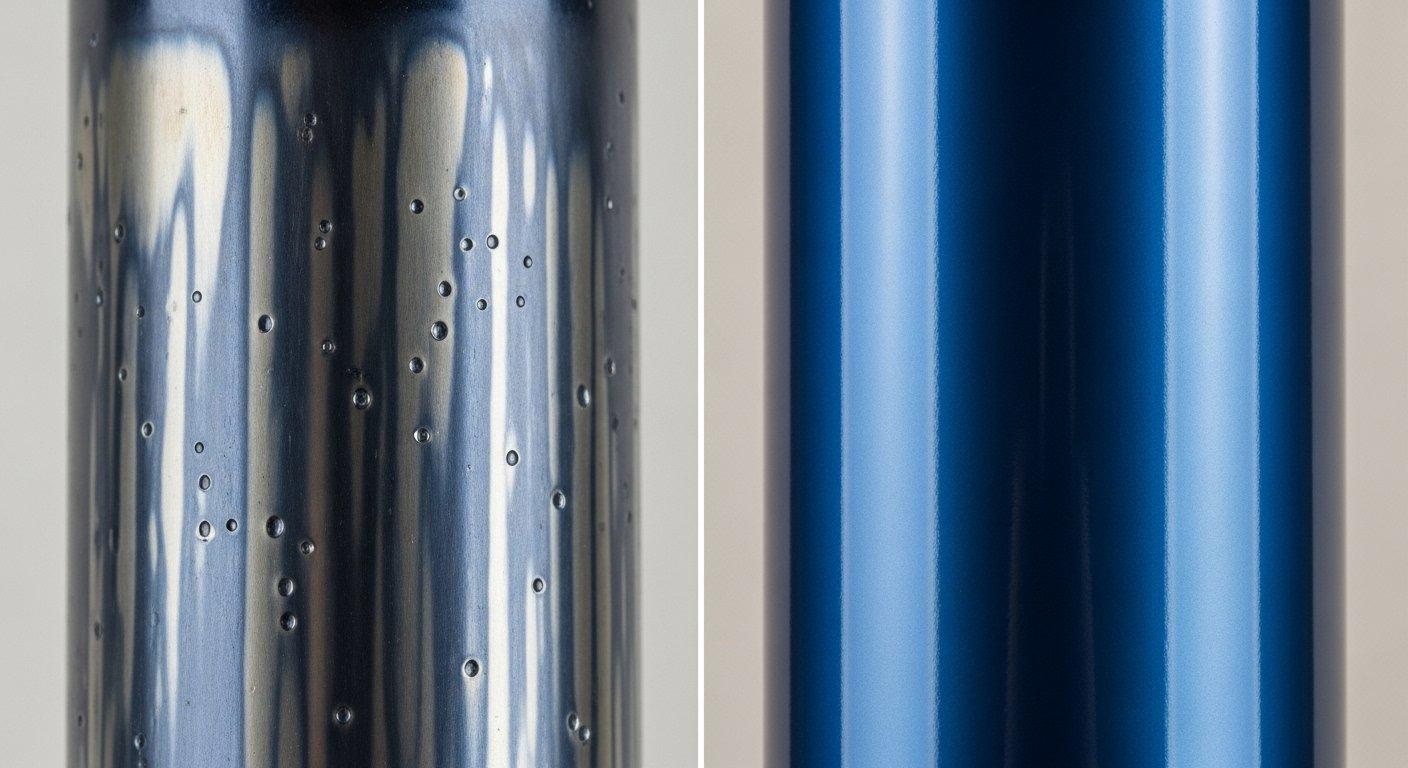
Avoiding color inconsistencies & defects
Achieving absolute color consistency across batches and ensuring defect-free surfaces is a common pain point in anodizing. This requires stringent process control, including precise regulation of electrolyte composition, temperature, and current density.
Careful material selection and meticulous cleaning protocols are also critical to prevent issues such as streaking, pitting, and non-uniform coloration.

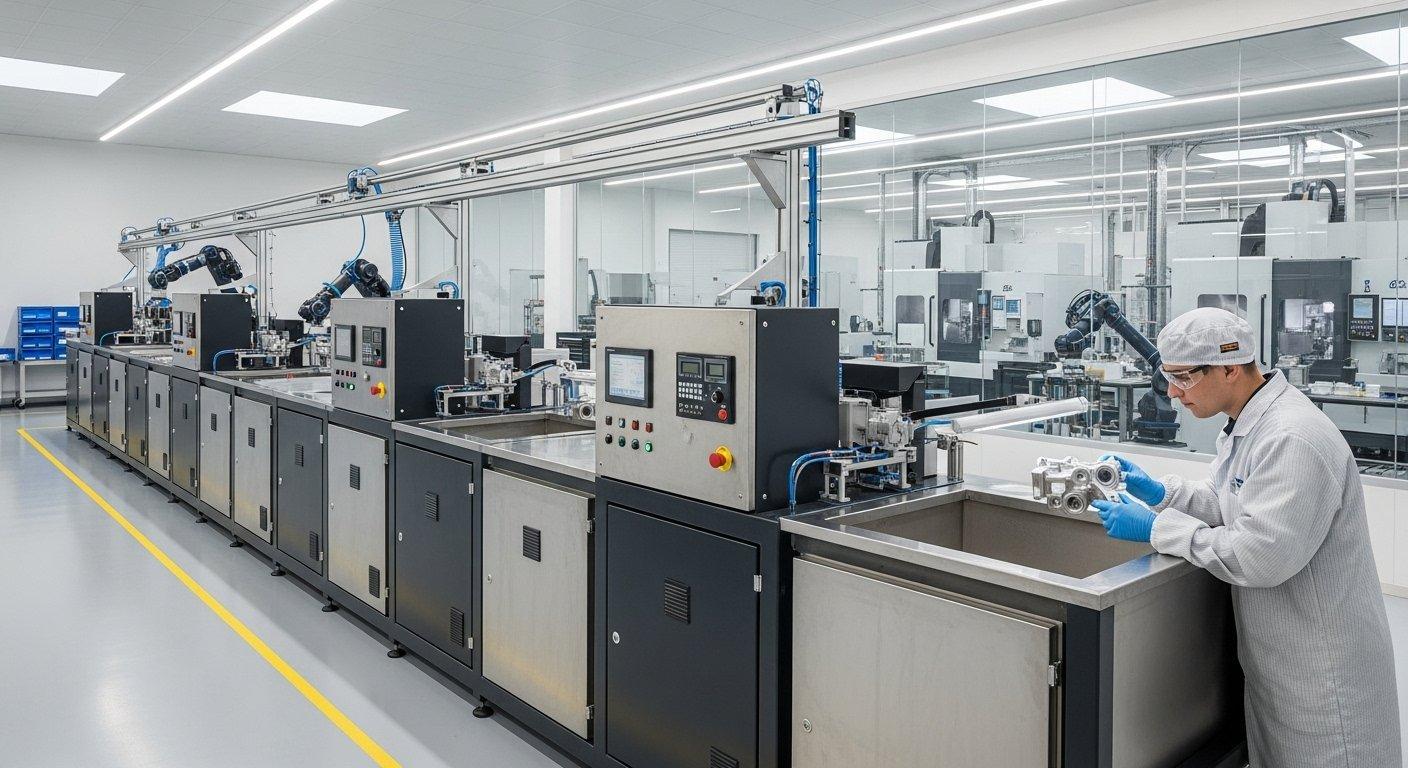
Ensuring repeatable, high-quality output
Repeatability and high-quality output are cornerstones of reliable manufacturing. For anodizing, this is achieved through robust quality assurance protocols and continuous monitoring of process parameters.
Regular bath analysis, consistent power supply, and automated control systems are vital to maintain the narrow operating windows required for consistent results batch after batch.
Expert Insights & Future Directions
Type II vs. Type III: selecting right
Selecting between Type II (Sulfuric Anodize) and Type III (Hard Coat Anodize) is a critical decision based on application requirements. Type II offers a thinner, aesthetic, and moderately protective layer.
Type III provides a much thicker, harder, and more wear-resistant layer, ideal for demanding industrial or military applications where extreme durability is paramount. The specific use case dictates the optimal anodizing process.
Type II Sulfuric Anodize vs. Type III Hard Coat Anodize
| Feature | Type II Sulfuric Anodize | Type III Hard Coat Anodize |
|---|---|---|
| **Thickness** | 0.0001 – 0.001 inches (2.5 – 25 µm) | 0.0005 – 0.004 inches (12.7 – 100 µm) |
| **Hardness (Vickers)** | 200-400 HV | 400-600 HV (can exceed 600 HV) |
| **Corrosion Resistance** | Good | Excellent |
| **Wear Resistance** | Good | Excellent |
| **Dyeing Capability** | Excellent | Limited (typically darker colors) |
| **Typical Applications** | Decorative, moderate protection | Industrial, military, high wear areas |
Advanced anodizing techniques explored
Beyond standard Type II and Type III, advanced anodizing techniques are continuously evolving to meet specialized demands. These can include specialized electrolyte compositions for enhanced properties or plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) for ceramic-like coatings.
Such methods push the boundaries of surface engineering, offering solutions for extreme environments or highly specific functional requirements.
Next Steps
Our Commitment to Excellence
High-quality parts, source expertise
As a source manufacturer, ‘ly-machining’ offers unparalleled expertise in CNC aluminum anodizing, ensuring the highest quality parts from initial machining to final surface treatment. Our integrated approach guarantees seamless production and superior outcomes.
We leverage deep technical knowledge to manage every aspect of your project, delivering components that exceed industry standards.
Transparent pricing, technical depth
We believe in transparent pricing and clear communication, providing detailed quotes without hidden fees. Our technical team offers profound insights and support, guiding clients through material selection and process optimization.
This commitment to clarity and technical depth ensures clients receive optimal value and solutions perfectly tailored to their specific needs.
Start Your Anodized Project
Request a quote & expert consultation
Initiating your next project with us is straightforward. Our experts are ready to provide a detailed consultation and help optimize your design for manufacturing.
We ensure a smooth transition from concept to high-quality finished product, backed by our comprehensive technical support.

Case Study: Ensuring Consistent Anodizing for High-Volume Medical Devices
**Problem:** A client, a manufacturer of precision medical diagnostic equipment, faced critical challenges with their previous supplier’s anodizing. They experienced persistent color inconsistencies and varying surface hardness across large batches of CNC machined aluminum housings. This led to costly rejections, production delays, and threatened their stringent regulatory compliance and brand reputation.
**Our Solution:** ‘ly-machining’ adopted an integrated approach, leveraging our expertise as a source manufacturer. Our engineers meticulously reviewed their design specifications and implemented a robust anodizing process. We established precise control over electrolyte composition, temperature, and current density for each batch, ensuring absolute process stability. Our in-house material scientists also collaborated to define optimal pre-treatment protocols for their specific aluminum alloy.
**Result:** The client achieved unprecedented consistency in both color and surface hardness for their anodized aluminum components. Our transparent pricing model provided clear cost breakdowns, and our predictable lead times eliminated production bottlenecks. The medical device manufacturer reported a 95% reduction in anodizing-related rejections, significantly cut costs, accelerated their time-to-market, and reinforced their confidence in a reliable, expert manufacturing partner.
Invite readers to get a free quote or technical consultation.
FAQ Section
What is CNC Aluminum Anodizing?
CNC Aluminum Anodizing is an electrochemical process that forms a protective, decorative oxide layer on aluminum parts. This layer is integral to the metal, providing superior corrosion and wear resistance compared to mere coatings.
The process involves submerging CNC machined aluminum components in an electrolyte bath and passing an electric current through them. This controlled oxidation enhances the material’s surface properties significantly.
What are main Anodized Aluminum Benefits?
The primary benefits of anodized aluminum include dramatically improved corrosion resistance, significantly increased surface hardness, and enhanced wear resistance. These properties extend the lifespan and reliability of components.
Additionally, anodizing offers aesthetic advantages, allowing for a wide anodizing color selection and a premium, consistent surface finish. This elevates both the functionality and visual appeal of parts.
Can I choose Anodizing Color Selection?
Yes, a vast anodizing color selection is available due to the porous nature of the anodic layer before sealing. Dyes can be absorbed into these pores to achieve a broad spectrum of colors.
Our technical team can guide you through the available color options and discuss any specific aesthetic requirements. We ensure color consistency across batches to meet your design specifications.