By exploring both sides of the equation, this piece aims to provide valuable insights that can help professionals navigate the complexities of aluminum machining. Whether you’re considering it for your next project or seeking ways to enhance your existing processes, understanding these pros and cons is essential for making informed decisions. With a balanced view of the material’s properties and the technological advancements shaping its use, this article offers a comprehensive look at aluminum machining in the current landscape, ensuring you’re well-prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. Join us as we break down the critical aspects of aluminum machining, equipping you with the knowledge necessary to leverage its full potential while mitigating possible downsides in 2025 and beyond.
What are the pros and cons of aluminum machining in 2025? This is a question that many in the manufacturing sector are asking as they navigate the increasingly complex landscape of materials and technology. Aluminum machining has become increasingly popular due to its unique properties, but it isn’t without its challenges. Let’s dive deeper into the essential pros and cons.
Advantages of Aluminum Machining
First, let’s start with the benefits. One of the most significant advantages of aluminum machining is its lightweight nature. A substantial reduction in weight can result in better fuel efficiency in automotive and aerospace applications. For example, when manufacturers utilize aluminum components instead of heavier alternatives, they often find significant improvements in performance metrics.
Another advantage is aluminum’s resistance to corrosion. It forms a protective oxide layer naturally, which helps prevent oxidation—meaning that parts last longer and require less maintenance over time. This property makes aluminum an excellent choice for outdoor applications or environments exposed to moisture.
Additionally, aluminum is highly machinable, meaning it can be shaped and formed easily, which is essential for prototyping and custom parts production. The versatility shown through different machining processes, such as CNC machining and die casting, enables manufacturers to meet a wide range of design specifications.
Lastly, in an era where sustainability is important, aluminum is recyclable without losing its properties, making it an environmentally responsible choice for businesses looking to reduce waste and energy consumption.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Machining
On the flip side, aluminum machining comes with its set of challenges. One major downside is the tendency of aluminum to deform under heat. When subjected to high-speed machining, the heat generated can cause the material to warp or change shape. As a result, careful temperature control and optimized machining parameters are essential to ensure precision.
Another concern is tool wear. Aluminum is softer than many other metals, but while it might seem easier to machine, it can also lead to faster tool degradation. High-speed machining of aluminum requires the use of specially coated tools and careful selection of speeds and feeds to reduce the occurrence of wear.
Moreover, the initial cost of quality aluminum can be higher than alternatives like steel, though this may be offset in the long run by the material’s durability and longevity. Companies must weigh the upfront costs versus potential savings in maintenance and replacement.
Lastly, while aluminum can be machined into intricate designs, achieving acceptable surface finishes can be tricky, often necessitating additional finishing processes to meet quality standards.
So, in summary, the pros and cons of aluminum machining in 2025 revolve around weighing its lightweight, corrosion-resistant benefits against challenges like deformation, tool wear, and cost. Understanding both sides will help businesses make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and goals.
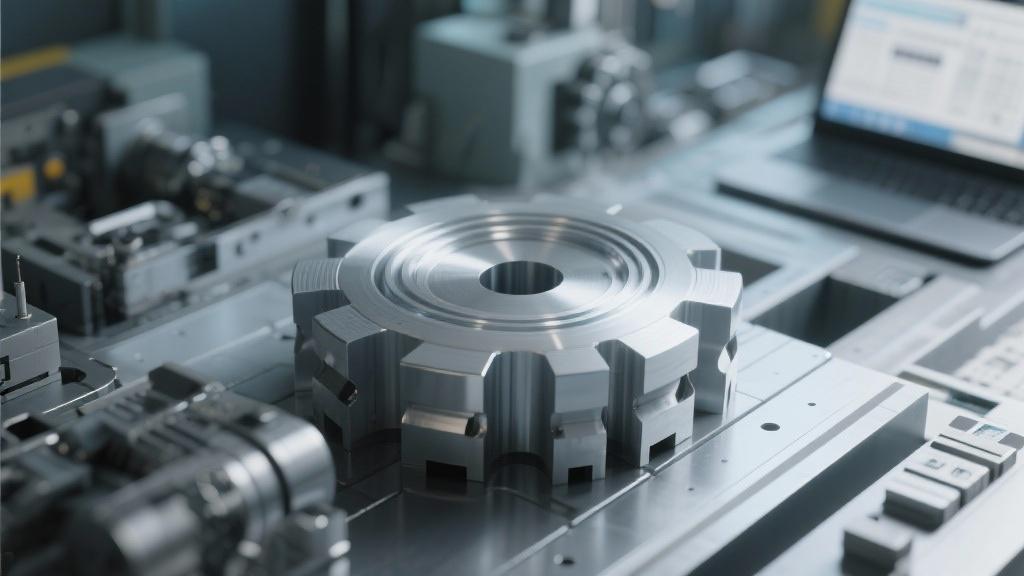
What are the main advantages of aluminum machining?
Aluminum machining offers several key advantages, such as its lightweight nature, which can enhance the performance of various applications, especially in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Another benefit is aluminum’s resistance to corrosion, which can significantly extend the longevity of parts and reduce maintenance needs in moist environments.
What challenges do manufacturers face when machining aluminum?
Manufacturers often encounter challenges such as the tendency for aluminum to deform under high heat during machining, requiring careful control of temperatures and machining parameters.
Moreover, tool wear can be a concern. Although aluminum is softer, it can still lead to faster wear of tools, necessitating the use of specially coated tools for various machining processes.
How does recycling affect the use of aluminum in machining?
Recycling plays a significant role in the use of aluminum, as the material can be recycled without losing its properties. This makes it an environmentally friendly choice for manufacturers looking to minimize waste.
Incorporating recycled aluminum can also lead to cost savings in materials while also supporting sustainability goals, which are increasingly important for many industries.
Is aluminum more expensive than other metals for machining?
While aluminum can have a higher initial cost compared to alternatives like steel, this cost can be offset by its durability and lower maintenance requirements over time.
Ultimately, organizations need to consider both the upfront investment and the potential long-term savings when making material decisions for machining processes.
How does the surface finish of aluminum compare to other materials?
Achieving a smooth surface finish in aluminum can be more challenging than in some other materials, often requiring additional finishing processes to meet quality standards.
This necessity for post-machining processes can impact cost and time, making it essential for manufacturers to plan accordingly when working with aluminum.




