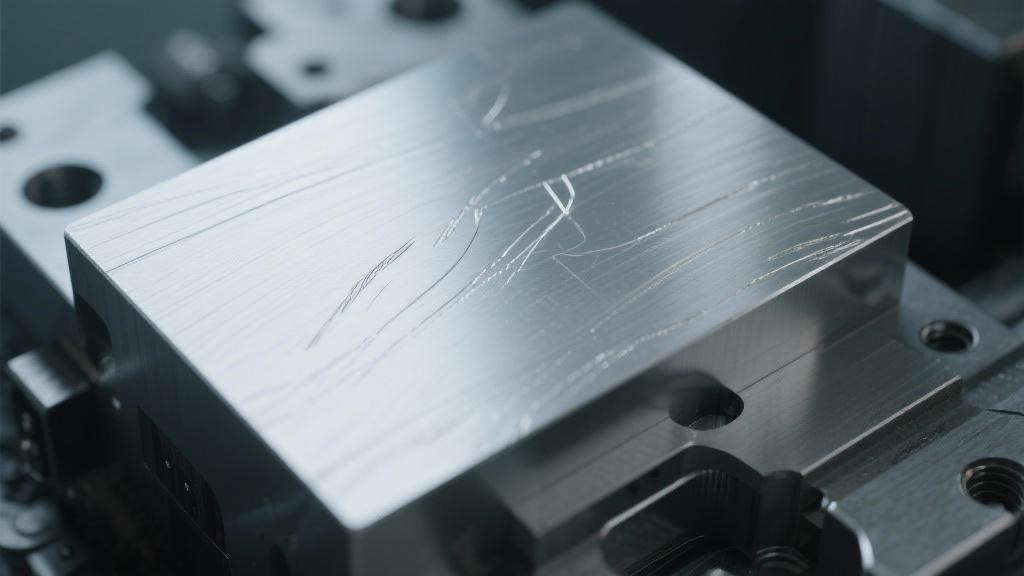
We will discuss the significance of maintaining optimal machining parameters and how even minor adjustments can lead to noticeable improvements. Additionally, we address common pitfalls that may result in undesirable tool marks and provide actionable strategies to minimize their occurrence. By understanding the underlying causes of tool marks, engineers and machinists can enhance their processes, ensuring that their aluminum components achieve the desired aesthetic and functional qualities.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting in the world of CNC machining, this comprehensive exploration will equip you with the knowledge needed to tackle tool marks effectively. Join us as we uncover the science behind these blemishes and learn how to achieve a superior finish that meets high standards in both performance and appearance.
When CNC machining aluminum, the appearance of tool marks can be a common frustration for many operators. You might have spent long hours perfecting your design, only to have the final product marred by these unsightly marks. Understanding why these tool marks occur is crucial for any machinist looking to achieve the highest quality finish on their components.
What Causes Tool Marks?
The formation of tool marks on aluminum surfaces during CNC machining can stem from a variety of factors. Firstly, the choice of tooling plays a significant role. Dull or improperly selected cutting tools often struggle to produce clean cuts, resulting in visible traces on the machined surface. Additionally, the properties of aluminum itself can contribute to how easily it can be cut and how it reacts to certain machining conditions.
Cutting Speed and Feed Rate
Two critical parameters that affect the smoothness of the finish are cutting speed and feed rate. If the cutting speed is too fast, it can create excessive friction, leading to tool wear and, subsequently, tool marks. Conversely, a feed rate that’s too slow might cause the tool to dwell in one spot for too long, producing uneven surfaces. Striking the right balance is crucial for achieving a polished look on aluminum ends.
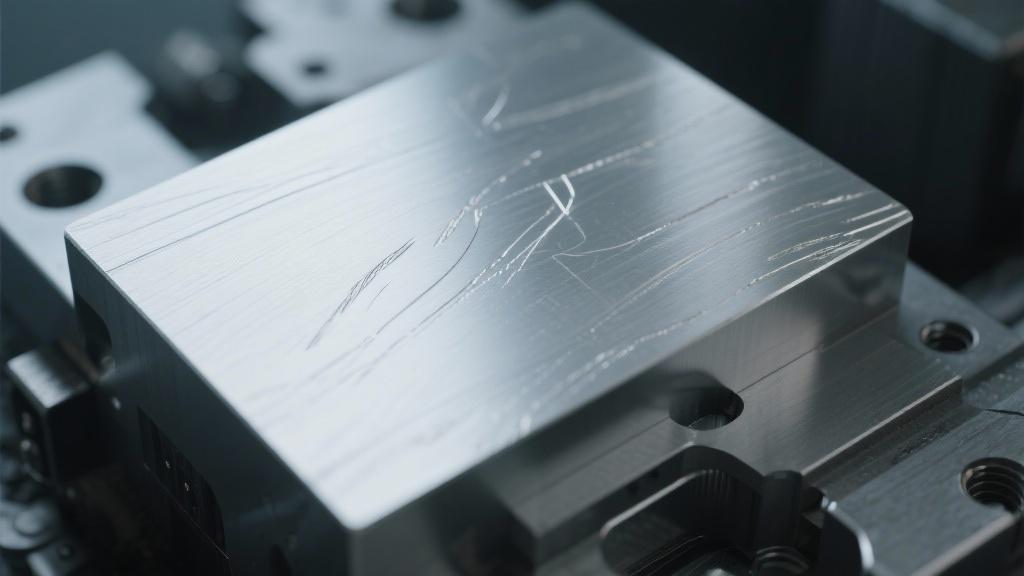

The Role of Coolant
Coolant usage also happens to be a major player in this equation. Proper application of cutting fluids helps lubricate the interface between the tool and the workpiece, minimizing heat generation and wear on the tool. If not used correctly, inadequate cooling can exacerbate tool wear, resulting in increased occurrence of tool marks. For effective results, make sure to choose the right type of coolant based on your machining operation and the type of aluminum you’re using.
Optimal Strategies for Mitigating Tool Marks
To mitigate tool marks, consider the following strategies:
Learning from Experience
In my own practice, I remember a project where tool marks greatly affected the appearance of my work. After some investigation, I realized the issue was due to outdated cutting tools and an improper feed rate. By recalibrating my machine and investing in new tooling, I saw a noticeable improvement. My experience aligns with studies from Machining Industry Publications emphasizing the need for precise tool management.
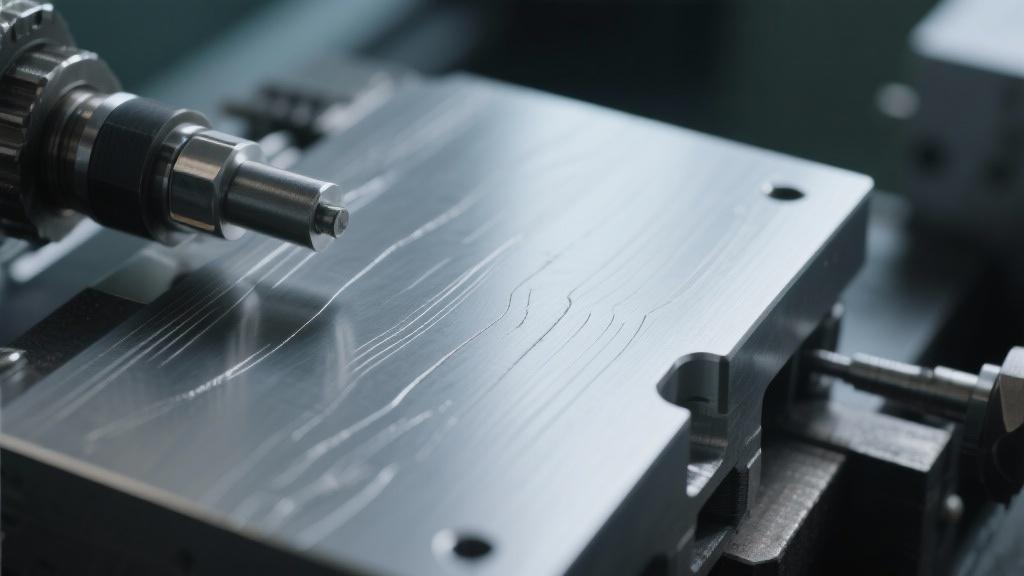
In conclusion, by understanding the causes of tool marks and actively managing your machining conditions, you can significantly enhance the surface quality of CNC machined aluminum parts. If you have any questions or want to share your own experiences, feel free to reach out! Engaging with your experiences could provide further insights that benefit the entire community.
What are the primary causes of tool marks on aluminum surfaces?
Tool marks on aluminum surfaces are mainly caused by dull cutting tools, incorrect cutting speeds, and inappropriate feed rates. When tools lose their sharpness, they tend to drag on the material rather than cutting cleanly, which results in visible marks.
Additionally, using the wrong type of tooling for aluminum can exacerbate the issue. It’s essential to choose tools designed specifically for aluminum machining to avoid these unpleasant surface imperfections.
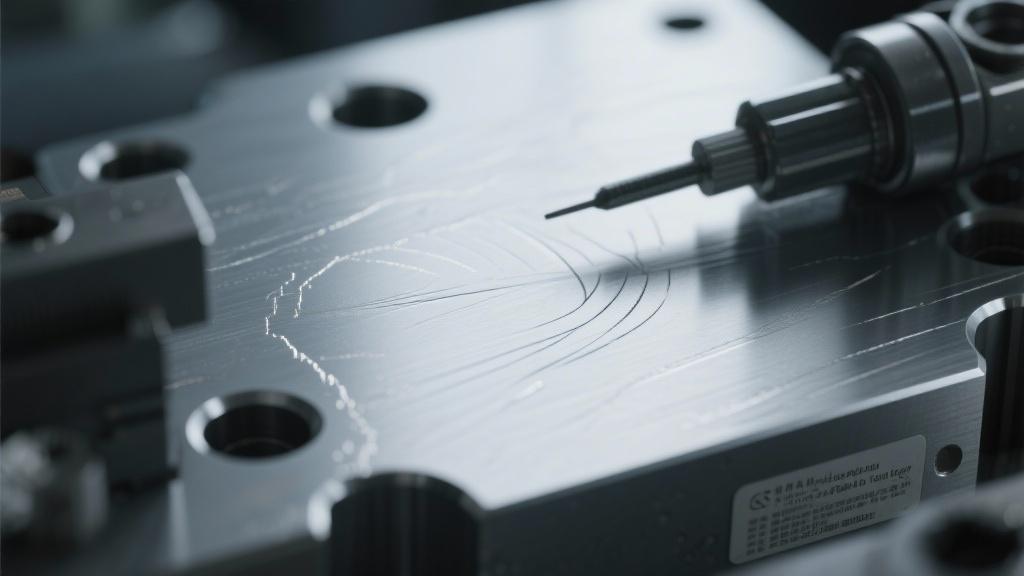
How does coolant impact the occurrence of tool marks?
Coolant plays a crucial role in preventing tool marks by reducing friction and heat during the machining process. Adequate coolant flow ensures that the cutting tool remains cool and adequately lubricated, promoting smoother cuts.
If the coolant is insufficient, it may lead to overheating of the tool, causing it to wear more rapidly and create rough surfaces. Therefore, using the right type of coolant in the correct amounts is vital for achieving a polished finish.
What strategies can I use to reduce tool marks on my machined components?
To minimize tool marks, consider using high-quality, sharp tooling and regularly maintain your cutting tools. Additionally, it’s important to adjust your machining parameters—like feed rate and cutting speed—to find the optimal settings for your specific project.
Moreover, implementing a suitable coolant strategy can make a significant difference. Ensuring that your machine is functioning correctly and that tools are calibrated will also enhance the quality of the final product.
Can you share any personal experiences related to tool marks and their solutions?
In my experience, I faced significant tool marks on aluminum parts when using old tooling and incorrect feed rates. Once I updated to new aluminum-specific cutting tools and adjusted my speeds, the surface finish improved dramatically.
This learning experience reinforced the importance of regular maintenance and attention to machining parameters. It’s often the small changes that lead to significant improvements in surface quality.




